- May. 11, 2025
Arid Land Geography ›› 2021, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1384-1395.doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000–6060.2021.05.19
• Earth Information Sciences • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Lirong1,ZHOU Dongmei1( ),CEN Guozhang1,MA Jing1,DANG Rui2,NI Fan1,ZHANG Jun1,3
),CEN Guozhang1,MA Jing1,DANG Rui2,NI Fan1,ZHANG Jun1,3
Received:2020-12-21
Revised:2021-04-26
Online:2021-09-25
Published:2021-09-22
Contact:
Dongmei ZHOU
E-mail:zhoudm@gsau.edu.cn
SUN Lirong,ZHOU Dongmei,CEN Guozhang,MA Jing,DANG Rui,NI Fan,ZHANG Jun. Landscape ecological risk assessment and driving factors of the Shule River Basin based on the geographic detector model[J].Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(5): 1384-1395.
Tab. 1
Formulas of landscape pattern indices"
| 景观格局指数 | 公式 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块个数(NP) |      | ni为景观要素i的斑块指数,反映景观中某一斑块类型的斑块总个数。其值越大表明景观破碎度越高。 |
| 聚集度指数(AI) |                    | gii和maxgii为基于单倍法的斑块类型i各像元之间节点数和最大节点数。AI约接近0时,斑块类型破碎度最大,凝聚程度越低;AI约接近100时,斑块类型越紧实。 |
| 最大斑块指数(LPI) |                       | max为景观中最大斑块的面积(km2);A为景观总面积(km2);an为第n个斑块。LPI反映最大斑块在景观中的优势比例。 |
| 景观形状指数(LSI) |              | Ei为第i种土地利用类型斑块边界的总长度(km),反映整体景观的形状复杂程度。LSI越接近于1,整体景观越简单;LSI越大,则斑块形状越不规则,越离散。 |
| 香农多样性指数(SHDI) |                | Pi为每一种斑块类型所占景观总面积的比例(%);n为景观中斑块类型的总数。SHDI反映斑块类型多样性,多样性指数越高表明景观中斑块类型越多。 |
| 香农均匀度指数(SHEI) |                           | m为土地利用类型数;pi为每一种斑块类型所占景观总面积的比例(%)。SHEI值较小时,反映景观受一种或几种优势斑块类型所支配;当SHEI趋于1时,说明景观中没有明显的优势类型且斑块类型在景观中均匀分布。 |
| 蔓延度指数(CONTAG) |      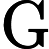                              | m为土地利用类型数;n为斑块数目;pij为随机选择的2个相邻栅格细胞是属于i和j的概率;CONTAG反映景观中不同类型斑块的团聚程度或延展趋势。 |
Tab. 2
Formulas of Landscape ecological risk indices"
| 指数名称 | 公式 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 景观生态风险指数(ERk) |                        | ERk为景观生态风险评价k的景观风险指数,值越大表示该评价单元的生态风险值越高,反之,值越低;Aki为景观生态风险评价单元k中第i类景观的面积(km2);Ak为评价单元k的总面积(km2);LLi为第i类景观的生态损失指数;m为景观类型的数量。 |
| 景观损失度指数(LLi) |          | LLi为景观损失度指数;Ci为破碎度指数;Ui为干扰度指数。 |
| 景观破碎度指数(Ci) |        | Ci为破碎度指数;ni为景观i的斑块数;Ai为景观i的总面积(km2)。 |
| 景观分离度指数(Fi) |               | Fi为景观分离度指数;A为景观总面积(km2);Ai为景观i的总面积(km2);ni为景观i的斑块数。 |
| 景观分维数(Di) |        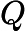        | Di为景观分维数;Qi为景观i的周长(km);Ai为景观i的总面积(km2)。 |
| 景观干扰度指数(Ui) |                  | Ui为景观干扰度指数;Ci为破碎度指数;Fi为景观分离度指数;Di为景观分维数;a、b、c分别为景观破碎度、分离度和分维数权重,对其赋值为0.5、0.3、0.2。 |
Tab. 3
Statistics of landscape pattern indices of patch types in the Shule River Basin from 2000 to 2018"
| 景观格局指数 | 年份 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 斑块个数(NP) | 2000 | 127 | 273 | 1736 | 138 | 85 | 281 |
| 2010 | 130 | 276 | 1775 | 146 | 84 | 293 | |
| 2018 | 126 | 261 | 1770 | 159 | 164 | 331 | |
| 最大斑块指数(LPI) | 2000 | 0.3014 | 0.0916 | 2.6584 | 0.1058 | 0.0373 | 78.1309 |
| 2010 | 0.3370 | 0.0916 | 2.6602 | 0.1058 | 0.0373 | 77.7646 | |
| 2018 | 0.4360 | 0.0810 | 2.7369 | 0.0997 | 0.0391 | 77.3710 | |
| 景观形状指数(LSI) | 2000 | 16.9571 | 17.549 | 58.4394 | 14.5510 | 10.4194 | 30.4054 |
| 2010 | 17.6835 | 18.0000 | 58.9516 | 14.7000 | 10.3548 | 30.7383 | |
| 2018 | 17.4118 | 17.6863 | 58.4410 | 15.2500 | 12.9730 | 31.1059 | |
| 聚集度指数(AI) | 2000 | 52.1012 | 30.1902 | 59.7878 | 41.2909 | 31.6159 | 90.1088 |
| 2010 | 56.1398 | 29.1667 | 59.5156 | 40.9483 | 32.4009 | 89.9689 | |
| 2018 | 59.8792 | 30.5306 | 59.6768 | 41.0032 | 31.5301 | 89.8246 |
Tab. 5
Statistics of the area and proportion of landscape ecological risk grades in the Shule River Basin from 2000 to 2018"
| 景观生态 风险等级 | 2000—2010年 | 2010—2018年 | 2000—2018年 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | |||
| 低 | -23.51 | -0.02 | 1154.71 | 1.03 | 1131.19 | 1.01 | ||
| 较低 | -37.16 | -0.03 | 1071.26 | 0.95 | 1034.10 | 0.92 | ||
| 中 | -5.03 | -0.01 | 2231.55 | 1.99 | 2226.52 | 1.98 | ||
| 较高 | -482.94 | -0.43 | -3230.81 | -2.88 | -3713.75 | -3.30 | ||
| 高 | 545.51 | 0.49 | -1228.21 | -1.09 | -682.71 | -0.61 | ||
Tab. 6
Interaction of driving factors of landscape ecological risk in the Shule River Basin from 2000 to 2018"
| 2000年 | 2010年 | 2018年 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 交互项 | 交互值 | 交互项 | 交互值 | 交互项 | 交互值 | 交互项 | 交互值 | 交互项 | 交互值 | 交互项 | 交互值 | ||
| X1∩X2 | 0.2474 | X3∩X5 | 0.3824 | X1∩X2 | 0.2421 | X3∩X5 | 0.3576 | X1∩X2 | 0.2554 | X3∩X5 | 0.2962 | ||
| X1∩X3 | 0.3492 | X3∩X6 | 0.3247* | X1∩X3 | 0.3327 | X3∩X6 | 0.3221* | X1∩X3 | 0.3163 | X3∩X6 | 0.2993 | ||
| X1∩X4 | 0.3760 | X3∩X7 | 0.2074* | X1∩X4 | 0.3692 | X3∩X7 | 0.2072* | X1∩X4 | 0.4459 | X3∩X7 | 0.2621* | ||
| X1∩X5 | 0.2479 | X3∩X8 | 0.6848 | X1∩X5 | 0.2334 | X3∩X8 | 0.7024 | X1∩X5 | 0.2909 | X3∩X8 | 0.5011 | ||
| X1∩X6 | 0.2364 | X4∩X5 | 0.3960 | X1∩X6 | 0.2327 | X4∩X5 | 0.3769 | X1∩X6 | 0.3028 | X4∩X5 | 0.4315 | ||
| X1∩X7 | 0.2092* | X4∩X6 | 0.3791* | X1∩X7 | 0.2082* | X4∩X6 | 0.3661* | X1∩X7 | 0.2713* | X4∩X6 | 0.4248 | ||
| X1∩X8 | 0.6456 | X4∩X7 | 0.2770* | X1∩X8 | 0.6934 | X4∩X7 | 0.2974* | X1∩X8 | 0.5239 | X4∩X7 | 0.2735 | ||
| X2∩X3 | 0.2423 | X4∩X8 | 0.6449 | X2∩X3 | 0.2464 | X4∩X8 | 0.6491 | X2∩X3 | 0.2613 | X4∩X8 | 0.5757 | ||
| X2∩X4 | 0.3166 | X5∩X6 | 0.2684 | X2∩X4 | 0.3249 | X5∩X6 | 0.2513 | X2∩X4 | 0.3276 | X5∩X6 | 0.2825 | ||
| X2∩X5 | 0.2680 | X5∩X7 | 0.2319* | X2∩X5 | 0.2535 | X5∩X7 | 0.2126* | X2∩X5 | 0.2499 | X5∩X7 | 0.2686* | ||
| X2∩X6 | 0.2352* | X5∩X8 | 0.6845 | X2∩X6 | 0.2227* | X5∩X8 | 0.7178 | X2∩X6 | 0.2489 | X5∩X8 | 0.5178 | ||
| X2∩X7 | 0.1136* | X6∩X7 | 0.1504* | X2∩X7 | 0.1064 | X6∩X7 | 0.1250* | X2∩X7 | 0.1663* | X6∩X7 | 0.2014* | ||
| X2∩X8 | 0.6507 | X6∩X8 | 0.6665 | X2∩X8 | 0.6794 | X6∩X8 | 0.6972 | X2∩X8 | 0.4608 | X6∩X8 | 0.5333 | ||
| X3∩X4 | 0.4148 | X7∩X8 | 0.5998 | X3∩X4 | 0.4221 | X7∩X8 | 0.6337 | X3∩X4 | 0.4325 | X7∩X8 | 0.4483* | ||
| [1] |
Cao Q, Zhang X, Lei D, et al. Multi-scenario simulation of landscape ecological risk probability to facilitate different decision-making preferences[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 227:325-335.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.125 |
| [2] | Turner M G. Landscape ecology: The effect of pattern on process[J]. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics, 2003, 20(1):171-197. |
| [3] | 谢小平, 陈芝聪, 王芳, 等. 基于景观格局的太湖流域生态风险评估[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(10):3369-3377. |
| [ Xie Xiaoping, Chen Zhicong, Wang Fang, et al. Ecological risk assessment of Taihu Lake Basin based on landscape pattern[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(10):3369-3377. ] | |
| [4] | 卢远, 苏文静, 华璀, 等. 左江上游流域景观生态风险评价[J]. 热带地理, 2010(5):38-44. |
| [ Lu Yuan, Su Wenjing, Hua Cui, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment for upper Zuojiang River Basin[J]. Tropical Geography, 2010(5):38-44. ] | |
| [5] | 江恩慧, 王远见, 田世民, 等. 流域系统科学初探[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(9):1026-1037. |
| [ Jiang Enhui, Wang Yuanjian, Tian Shiming, et al. Exploration of watershed system science[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(9):1026-1037. ] | |
| [6] |
曹祺文, 张曦文, 马洪坤, 等. 景观生态风险研究进展及基于生态系统服务的评价框架: ESRISK[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(5):843-855.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201805005 |
|
[ Cao Qiwen, Zhang Xiwen, Ma Hongkun, et al. Review of landscape ecological risk and an assessment framework based on ecological services: ESRISK[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(5):843-855. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201805005 |
|
| [7] |
Wang H, Liu X M, Zhao C Y, et al. Spatial-temporal pattern analysis of landscape ecological risk assessment based on land use/land cover change in Baishuijiang National Nature Reserve in Gansu Province, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 124:107454, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107454.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107454 |
| [8] |
Vinod K, Anket S, Shevita P, et al. A review of ecological risk assessment and associated health risks with heavy metals in sediment from India[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2020, 35(5):516-526.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2020.03.012 |
| [9] |
陈峰, 李红波, 张安录. 基于生态系统服务的中国陆地生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3):432-445.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201903003 |
|
[ Chen Feng, Li Hongbo, Zhang Anlu. Ecological risk assessment based on terrestrial ecosystem services in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(3):432-445. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201903003 |
|
| [10] | 张月, 张飞, 周梅, 等. 干旱区内陆艾比湖区域景观生态风险评价及时空分异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1):233-242. |
| [ Zhang Yue, Zhang Fei, Zhou Mei, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its spatio-temporal variations in Ebinur Lake region of inland arid area[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(1):233-242. ] | |
| [11] |
Xing L, Hu M S, Wang Y. Integrating ecosystem services value and uncertainty into regional ecological risk assessment: A case study of Hubei Province, Central China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 740:140126, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140126.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140126 |
| [12] | 马胜, 梁小英, 刘迪, 等. 生态脆弱区多尺度景观生态风险评价--以陕西省米脂县高渠乡为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(10):3171-3178. |
| [ Ma Sheng, Liang Xiaoying, Liu Di, et al. Multi-scale landscape ecological risk assessment in ecologically fragile regions: A case study in Gaoqu Town in Mizhi County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(10):3171-3178. ] | |
| [13] |
Arenas-Sánchez A, Rico A, Rivas-Tabares D, et al. Identification of contaminants of concern in the upper Tagus River Basin (central Spain). Part 2: Spatio-temporal analysis and ecological risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 667:222-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.286 |
| [14] |
Ayre K K, Landis W G. A Bayesian approach to landscape ecological risk assessment applied to the Upper Grande Ronde Watershed, Oregon[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 2012, 18(5):946-970.
doi: 10.1080/10807039.2012.707925 |
| [15] | Chow T E, Gaines K F, Hodgson M E. et al. Habitat and exposure modelling for ecological risk assessment: A case study for the raccoon on the Savannah River site[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2005, 189(1-2):151-167. |
| [16] |
彭建, 党威雄, 刘焱序, 等. 景观生态风险评价研究进展与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(4):664-677.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201504013 |
|
[ Peng Jian, Dang Weixiong, Liu Yanxu, et al. Review on landscape ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(4):664-677. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201504013 |
|
| [17] |
Yang T, Zhang Q, Wan X B, et al. Comprehensive ecological risk assessment for semi-arid basin based on conceptual model of risk response and improved TOPSIS model: A case study of Wei River Basin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719:137502, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137502.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137502 |
| [18] |
李青圃, 张正栋, 万露文, 等. 基于景观生态风险评价的宁江流域景观格局优化[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(7):1420-1437.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201907011 |
|
[ Li Qingpu, Zhang Zhengdong, Wan Luwen, et al. Landscape pattern optimization in Ningjiang River Basin based on landscape ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(7):1420-1437. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201907011 |
|
| [19] | 郑杰, 王志杰, 喻理飞, 等. 基于景观格局的草海流域生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4):784-792. |
| [ Zheng Jie, Wang Zhijie, Yu Lifei, et al. Ecological risk assessment of Caohai Watershed based on landscape pattern[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4):784-792. ] | |
| [20] |
王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1):116-134.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010 |
|
[ Wang Jinfeng, Xu Chengdong. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1):116-134. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010 |
|
| [21] |
Wang J F, Li X H, Christakos G, et al. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2010, 24(1):107-127.
doi: 10.1080/13658810802443457 |
| [22] |
Tian F, Liu L Z, Yang J H, et al. Vegetation greening in more than 94% of the Yellow River Basin (YRB) region in China during the 21st century caused jointly by warming and anthropogenic activities[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 125:107479, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107479.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107479 |
| [23] | 罗瑶, 彭文甫, 董永波, 等. 基于地理探测器下的川西高原地表温度空间格局及影响因子分析--以西昌市为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(3):738-749. |
| [ Luo Yao, Peng Wenfu, Dong Yongbo, et al. Geographical exploration of the spatial pattern of the surface temperature and its influencing factors in western Sichuan Plateau: A case of Xichang City[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(3):738-749. ] | |
| [24] |
Xu L, Du H R, Zhang X L. Driving forces of carbon dioxide emissions in China’s cities: An empirical analysis based on the geodetector method[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 287:125169, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125169.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125169 |
| [25] | 潘洪义, 黄佩, 徐婕. 基于地理探测器的岷江中下游地区植被NPP时空格局演变及其驱动力研究[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20):7621-7631. |
| [ Pan Hongyi, Huang Pei, Xu Jie. The spatial and temporal pattern evolution of vegetation NPP and its driving forces in middle-lower areas of the Min River based on geographical detector analyses[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20):7621-7631. ] | |
| [26] |
Yuan L H, Chen X Q, Wang X Y, et al. Spatial associations between NDVI and environmental factors in the Heihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019, 29(9):1548-1564.
doi: 10.1007/s11442-019-1676-0 |
| [27] | 张思源, 聂莹, 张海燕, 等. 基于地理探测器的内蒙古植被NDVI时空变化与驱动力分析[J]. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5):1460-1472. |
| [ Zhang Siyuan, Nie Ying, Zhang Haiyan, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation NDVI and its driving forces in Inner Mongolia based on geodetector[J]. Acta Grasslandica, 2020, 28(5):1460-1472. ] | |
| [28] | 孙道亮, 洪步庭, 任平. 都江堰市农村居民点时空演变与驱动因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(10):2167-2176. |
| [ Sun Daoliang, Hong Buting, Ren Ping. Study on the spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of rural settlements in Dujiangyan City[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2020, 29(10):2167-2176. ] | |
| [29] |
Xie Z X, Qin Y C, Li Y, et al. Spatial and temporal differentiation of COVID-19 epidemic spread in mainland China and its influencing factors[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 744:140929, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140929.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140929 |
| [30] | 王琳, 赵俊三. 城市群新冠疫情时空分布格局与分异机制的地理探测[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(19):6788-6800. |
| [ Wang Lin, Zhao Junsan. Spatiotemporal distribution pattern of the COVID-19 epidemic and geographical detection[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(19):6788-6800. ] | |
| [31] | 潘竟虎, 胡艳兴. 疏勒河中下游近35年土地利用与景观格局动态[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(4):742-748. |
| [ Pan Jinghu, Hu Yanxing. Dynamic change of land use & landscape pattern in middle and lower reaches of Shule River during recent 35 years[J]. Soils, 2014, 46(4):742-748. ] | |
| [32] | 吴金华, 房世峰, 刘宝军, 等. 乌裕尔河-双阳河流域湿地景观格局演变及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13):4279-4290. |
| [ Wu Jinhua, Fang Shifeng, Liu Baojun, et al. Landscape pattern evolution of wetland and its driving mechanism in Wuyuer-Shuangyang River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(13):4279-4290. ] | |
| [33] | 贾艳艳, 唐晓岚, 刘振威, 等. 1995-2016年长江沿岸芜湖区段景观格局梯度分析[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2020, 39(4):115-121. |
| [ Jia Yanyan, Tang Xiaolan, Liu Zhenwei, et al. Gradient analysis of landscape pattern in Wuhu Section along the Yangtze River from 1995 to 2016[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2020, 39(4):115-121. ] | |
| [34] | 徐启渝, 王鹏, 王涛, 等. 土地利用结构与景观格局对鄱阳湖流域赣江水质的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4):1008-1019. |
| [ Xu Qiyu, Wang Peng, Wang Tao, et al. Investigation of the impacts of land use structure and landscape pattern on water quality in the Ganjiang River, Poyang Basin[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2020, 32(4):1008-1019. ] | |
| [35] | 秦艳丽, 时鹏, 何文虹, 等. 西安市城市化对景观格局及生态系统服务价值的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(22):1-12. |
| [ Qin Yanli, Shi Peng, He Wenhong, et al. Influence of urbanization on landscape pattern and ecosystem service value in Xi’an City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(22):1-12. ] | |
| [36] | 娄妮, 王志杰, 何嵩涛. 基于景观格局的阿哈湖国家湿地公园景观生态风险评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(1):233-239. |
| [ Lou Ni, Wang Zhijie, He Songtao. Assessment on ecological risk of Aha Lake National Wetland Park based on landscape pattern[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(1):233-239. ] | |
| [37] | 王涛, 肖彩霞, 刘娇, 等. 杞麓湖流域景观时空格局演变及其对景观生态风险的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(6):219-225. |
| [ Wang Tao, Xiao Caixia, Liu Jiao, et al. Evolution of spatial and temporal patterns of landscape and its impact on landscape ecological risk in Qilu Lake Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(6):219-225. ] | |
| [38] |
Zhang C Q, Dong B, Liu L P, et al. Study on ecological risk assessment for land-use of wetland based on different scale[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2015, 44(5):1-8.
doi: 10.1007/s12524-015-0448-2 |
| [39] | 陈鹏, 傅世锋, 文超祥, 等. 1989-2010年间厦门湾滨海湿地人为干扰影响评价及景观响应[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2014, 33(2):167-174. |
| [ Chen Peng, Fu Shifeng, Wen Chaoxiang, et al. Assessment of the impact on coastal wetland of Xiamen Bay and response of landscape pattern from human disturbance from 1989 to 2010[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2014, 33(2):167-174. ] | |
| [40] | 孙永光, 赵冬至, 吴涛, 等. 河口湿地人为干扰度时空动态及景观响应--以大洋河口为例[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(12):3645-3655. |
| [ Sun Yongguang, Zhao Dongzhi, Wu Tao, et al. Temporal and spatial dynamic changes and landscape pattern response of hemeroby in Dayang estuary of Liaoning Province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(12):3645-3655. ] | |
| [41] | 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):791-799. |
| [ Pan Jinghu, Liu Xiao. Landscape ecological risk assessment and landscape security pattern optimization in Shule River Basin[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3):791-799. ] | |
| [42] | 康紫薇, 张正勇, 位宏, 等. 基于土地利用变化的玛纳斯河流域景观生态风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(18):6472-6485. |
| [ Kang Ziwei, Zhang Zhengyong, Wei Hong, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment in Manas River Basin based on land use change[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(18):6472-6485. ] | |
| [43] | 位宏, 徐丽萍, 李晓蕾, 等. 博斯腾湖流域景观生态风险评价与时空变化[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(增刊1):345-351. |
| [ Wei Hong, Xu Liping, Li Xiaolei, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its spatiotemporal changes of the Bosten Lake Basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(Suppl.1):345-351. ] | |
| [44] | 巩杰, 谢余初, 赵彩霞, 等. 甘肃白龙江流域景观生态风险评价及其时空分异[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(8):2153-2160. |
| [ Gong Jie, Xie Yuchu, Zhao Caixia, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its spatiotemporal variation of Bailong Watershed, Gansu[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(8):2153-2160. ] | |
| [45] | 刘世梁, 刘琦, 张兆苓, 等. 云南省红河流域景观生态风险及驱动力分析[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(13):3728-3734. |
| [ Liu Shiliang, Liu Qi, Zhang Zhaoling, et al. Landscape ecological risk and driving force analysis in Red River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(13):3728-3734. ] | |
| [46] | 黄木易, 何翔. 近20年来巢湖流域景观生态风险评估与时空演化机制[J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(4):785-793. |
| [ Huang Muyi, He Xiang. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its mechanism in Chaohu Basin during the past almost 20 years[J]. Lake Science, 2016, 28(4):785-793. ] | |
| [47] | 吕乐婷, 张杰, 孙才志, 等. 基于土地利用变化的细河流域景观生态风险评估[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(16):5952-5960. |
| [ Lü Leting, Zhang Jie, Sun Caizhi, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment of Xi River Basin based on land-use change[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(16):5952-5960. ] | |
| [48] | 张学斌, 石培基, 罗君, 等. 基于景观格局的干旱内陆河流域生态风险分析--以石羊河流域为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(3):410-419. |
| [ Zhang Xuebin, Shi Peiji, Luo Jun, et al. The ecological risk analysis of arid inland river basin at the landscape scale: A case study on Shiyang River Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(3):410-419. ] | |
| [49] | 奚世军. 喀斯特山区流域综合生态风险评估及其驱动力分析--以贵州乌江流域为例[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2020. |
| [ Xi Shijun. Comprehensive ecological risk assessment and driving force analysis of karst mountain basin: A case study of Wujiang River Basin, Guizhou Province[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2020. ] | |
| [50] | 郑续, 魏乐民, 郭建军, 等. 基于地理探测器的干旱区内陆河流域产水量驱动力分析--以疏勒河流域为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(6):1477-1485. |
| [ Zheng Xu, Wei Lemin, Guo Jianjun, et al. Driving force analysis of water yield in inland river basins of arid areas based on geo-detectors: A case of the Shule River[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(6):1477-1485. ] |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 1546
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 603
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||
