- May. 14, 2025
Arid Land Geography ›› 2024, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (10): 1767-1780.doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2024.058
• Regional Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-01-25
Revised:2024-04-07
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
LI Boya
E-mail:1836160272@163.com;bylkkkk@163.com
SHI Weiliang, LI Boya. Resilience spatial network structure of the three major urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin[J].Arid Land Geography, 2024, 47(10): 1767-1780.
Tab. 1
Evaluation index system of urban resilience based on DPSR model"
| 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | 描述与说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 驱动力 | 经济发展驱动力 | GDP增长率(+) | 经济活力 |
| 第三产业增加值(+) | 产业结构 | ||
| 固定资产投资增长率(+) | 生产要素保障 | ||
| 国内外3种专利授权数(+) | 技术进步 | ||
| 社会发展驱动力 | 城镇化率(+) | 社会进步水平和经济发展水平 | |
| 人口增长率(+) | 社会经济增长的基本要素 | ||
| 城镇居民人均可支配收入(+) | 居民消费驱动力 | ||
| 一般公共预算支出(+) | 社会发展驱动力 | ||
| 压力 | 经济社会压力 | 失业率(-) | 就业风险 |
| 外贸依存度(-) | 外部安全风险 | ||
| 人口密度(-) | 人口压力 | ||
| 生态资源压力 | SO2排放(-) | 环境污染及能源压力 | |
| 废气排放(-) | |||
| 单位生产总值能耗(-) | |||
| 状态 | 城市环境资源状态 | 城市人均园林绿地面积(+) | 城市基础生态状况 |
| 空气质量优良天数比例(+) | |||
| 城市用水普及率(+) | 城市能源使用情况 | ||
| 燃气普及率(+) | |||
| 城市经济社会状态 | 职工平均工资(+) | 社会状态 | |
| 城市恩格尔系数(+) | |||
| 人均GDP(+) | 经济状态 | ||
| 政府财政收入增长率(+) | |||
| 城市基础设施状态 | 建成区排水管道密度(+) | 排水情况 | |
| 人均城市道路面积(+) | 道路交通状况 | ||
| 响应 | 抵抗、恢复能力 | 互联网普及程度(+) | 预警与救援能力 |
| 千人拥有的卫生机构病床数(+) | |||
| 社会保障占公共预算支出比例(+) | |||
| 人均金融机构存款(+) | |||
| 污水处理率(+) | 污染治理能力 | ||
| 生活垃圾无害处理率(+) | |||
| 适应响应 | 科学教育事业投入占GDP比重指标(+) | 经济创新 | |
| 城市市政公用设施建设固定资产投资完成额指标(+) | 基础设施 | ||
| 居民年末储蓄余额(+) | 社会提升 |
Tab. 2
Resilience development trends of the three major urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin from 2012 to 2021"
| 城市群 | 2012年 | 2013年 | 2014年 | 2015年 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 | 增幅 | 增速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山东半岛城市群 | 0.266 | 0.274 | 0.279 | 0.291 | 0.306 | 0.320 | 0.335 | 0.348 | 0.372 | 0.419 | 0.123 | 0.575 |
| 中原城市群 | 0.214 | 0.220 | 0.223 | 0.234 | 0.247 | 0.270 | 0.288 | 0.297 | 0.313 | 0.329 | 0.108 | 0.450 |
| 关中平原城市群 | 0.218 | 0.223 | 0.223 | 0.229 | 0.239 | 0.242 | 0.254 | 0.265 | 0.277 | 0.297 | 0.078 | 0.282 |
Tab. 4
Resilience network density matrix and image matrix of the three major urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin"
| 城市群 | 年份 | 板块 | 网络密度矩阵 | 像矩阵 | 韧性关联网络简化图 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 板块一 | 板块二 | 板块三 | 板块四 | 板块一 | 板块二 | 板块三 | 板块四 | |||||
| 山东半岛城市群 | 2012 | 板块一 | 0.300 | 0.500 | 0.067 | 0.050 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 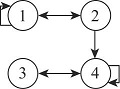 | |
| 板块二 | 0.500 | 0.167 | 0.000 | 0.188 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.417 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| 板块四 | 0.000 | 0.250 | 0.417 | 0.333 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 2021 | 板块一 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.333 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |  | ||
| 板块二 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.000 | 0.200 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.583 | 0.333 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 板块四 | 0.083 | 0.267 | 0.250 | 0.333 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 中原城市群 | 2012 | 板块一 | 0.881 | 0.321 | 0.000 | 0.229 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |  | |
| 板块二 | 0.321 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.050 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.467 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| 板块四 | 0.229 | 0.050 | 0.467 | 0.500 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 2021 | 板块一 | 1.000 | 0.667 | 0.417 | 0.278 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 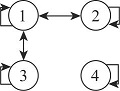 | ||
| 板块二 | 0.667 | 0.800 | 0.000 | 0.111 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.417 | 0.000 | 0.583 | 0.167 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 板块四 | 0.333 | 0.111 | 0.167 | 0.533 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| 关中平原城市群 | 2012 | 板块一 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 0.000 | - | 1 | 1 | 0 | - |  | |
| 板块二 | 0.250 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | ||||
| 2021 | 板块一 | 1.000 | 0.250 | 0.000 | - | 1 | 1 | 0 | - | 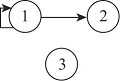 | ||
| 板块二 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | ||||
| 板块三 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | ||||
| [1] | Alberti M. The effects of urban patterns on ecosystem function[J]. International Regional Science Review, 2005, 28(2): 168-192. |
| [2] | Cutter S L, Barnes L, Berry M, et al. A place based model for understanding community resilience to natural disasters[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2008(18): 598-606. |
| [3] | 范玲, 闫绪娴, 王俊丽, 等. 韧性城市建设的国际经验、中国困境与应对策略[J]. 城市问题, 2022, 323(6): 95-103. |
| [Fan Ling, Yan Xuxian, Wang Junli, et al. International experience of resilient city construction, China’s dilemma and coping strategies[J]. Urban Problem, 2022, 323(6): 95-103.] | |
| [4] | 刘彦平. 城市韧性系统发展测度——基于中国288个城市的实证研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2021, 28(6): 93-100. |
| [Liu Yanping. Urban resilience system development measurement: Based on an empirical study of 288 Chinese cities[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2021, 28(6): 93-100.] | |
| [5] |
赵瑞东, 方创琳, 刘海猛. 城市韧性研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(10): 1717-1731.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.011 |
|
[Zhao Ruidong, Fang Chuanglin, Liu Haimeng. Progress and prospect of urban resilience research[J]. Progress in Geography, 2020, 39(10): 1717-1731.]
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.011 |
|
| [6] |
白立敏, 修春亮, 冯兴华, 等. 中国城市韧性综合评估及其时空分异特征[J]. 世界地理研究, 2019, 28(6): 77-87.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.06.2018403 |
|
[Bai Limin, Xiu Chunliang, Feng Xinghua, et al. A comprehensive assessment of urban resilience and its spatial differentiation in China[J]. World Regional Studies, 2019, 28(6): 77-87.]
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.06.2018403 |
|
| [7] | Joerin J, Shaw R, Takeuchi Y, et al. Action oriented resilience assessment of communities in Chennai, India[J]. Environmental Hazards, 2012, 11(3): 226-241. |
| [8] | 张振, 张以晨, 张继权, 等. 基于熵权法和TOPSIS模型的城市韧性评估: 以长春市为例[J]. 灾害学, 2023, 38(1): 213-219. |
| [Zhang Zhen, Zhang Yichen, Zhang Jiquan, et al. Urban resilience assessment based on entropy weight method and TOPSIS model: Take Changchun City as an example[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2023, 38(1): 213-219.] | |
| [9] | 朱金鹤, 孙红雪. 中国三大城市群城市韧性时空演进与影响因素研究[J]. 软科学, 2020, 34(2): 72-79. |
| [Zhu Jinhe, Sun Hongxue. Study on spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban resilience of China’s three metropolitan agglomerations[J]. Soft Science, 2020, 34(2): 72-79.] | |
| [10] | Wilda Sky A. Searching for safety[M]. New Brunswick N J: Transaction, 1991: 25-29. |
| [11] | Godschalk D R. Urban hazard mitigation: Creating resilience cities[J]. Natural Hazards, 2003(4): 136-143. |
| [12] | 缪惠全, 王乃玉, 汪英俊, 等. 基于灾后恢复过程解析的城市韧性评价体系[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2021, 30(1): 10-27. |
| [Miao Huiquan, Wang Naiyu, Wang Yingjun, et al. An urban resilience measurement system based on decomposing post-disaster recovery process[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(1): 10-27.] | |
| [13] | 朱诗尧. 城市抗涝韧性的度量与提升策略研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021. |
| [Zhu Shiyao. Evauation and impmprovement starovement strategy of urban flood resilience[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.] | |
| [14] | 尹建军, 胡静, 黄宇瑄. 长江中游城市群城市韧性时空演化特征及动态预测研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2023, 32(11): 2312-2325. |
| [Yin Jianjun, Hu Jing, Huang Yuxuan. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and dynamic prediction of urban resilience in urban agglomerations in middle reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2023, 32(11): 2312-2325.] | |
| [15] | 王彩丽, 闫绪娴. 成渝城市群城市韧性时空格局演变及障碍因子识别[J]. 重庆大学学报(社会科学版), 2023, 29(3): 21-33. |
| [Wang Caili, Yan Xuxian. Spatiotemporal revolution and obstacles identification of urban resilience in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Chongqing University (Social Science Edition), 2023, 29(3): 21-33.] | |
| [16] | 石宇. 京津冀城市群韧性资源网络结构特征与影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2022. |
| [Shi Yu. Research on the structural characteristics and influencing factors of resilience resources network of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2022.] | |
| [17] | 王逸舟, 王海军, 张彬, 等. 基于多维要素流视角的城市群网络结构及影响因素分析——以武汉城市圈为例[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(6): 68-76. |
| [Wang Yizhou, Wang Haijun, Zhang Bin, et al. Analysis on the network structure of urban agglomeration and its influencing factors based on the perspective of multi-dimensional feature flow: Taking Wuhan urban agglomeration as an example[J]. Economic Geography, 2021, 41(6): 68-76.] | |
| [18] | 鲍进剑, 梁娟珠, 周玉科, 等. 多元交通流视角下长江经济带城市网络空间组织模式分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2023, 39(2): 46-54, 143. |
| [Bao Jinjian, Liang Juanzhu, Zhou Yuke, et al. Spatial organization pattern of urban network in the Yangtze River economic belt from the perspective of multiple traffic flows[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2023, 39(2): 46-54, 143.] | |
| [19] | 吴思雨. 流空间视角下的长江中游城市群网络结构研究[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2021. |
| [Wu Siyu. Research on the network structure of the city groups in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River from the perspective of flow space[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2021.] | |
| [20] | 李硕硕, 刘耀彬, 骆康. 生态安全约束下环鄱阳湖区城市经济韧性的空间关联网络特征[J]. 生态经济, 2023, 39(4): 95-102. |
| [Li Shuoshuo, Liu Yaobin, Luo Kang. Spatial correlation network characteristics of urban economic resilience in Poyang Lake region under the ecological security constraints[J]. Ecological Economy, 2023, 39(4): 95-102.] | |
| [21] |
李艳, 孙阳, 陈雯. 反身性视角下信息流空间建构与网络韧性分析: 以长三角百度用户热点搜索为例[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2021, 38(1): 62-72.
doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.01.009 |
|
[Li Yan, Sun Yang, Chen Wen. Construction of space of information flows and assessment of network resilience from reflexive perspective: A case study of Baidu index in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 38(1): 62-72.]
doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.01.009 |
|
| [22] |
谢永顺, 王成金, 韩增林, 等. 哈大城市带网络结构韧性演化研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(10): 1619-1631.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.002 |
|
[Xie Yongshun, Wang Chengjin, Han Zenglin, et al. Structural resilience evolution of multiple urban networks in the Harbin-Dalian urban belt[J]. Progress in Geography, 2020, 39(10): 1619-1631.]
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.002 |
|
| [23] |
周成, 赵亚玲, 张旭红, 等. 黄河流域城市生态韧性与效率时空演化特征及协调发展分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(9): 1514-1523.
doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.633 |
|
[Zhou Cheng, Zhao Yaling, Zhang Xuhong, et al. Spatiotemporal evolutionary characteristics and coordinated development of urban ecological resilience and efficiency in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(9): 1514-1523.]
doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.633 |
|
| [24] | 杨秀平, 王里克, 李亚兵, 等. 韧性城市研究综述与展望[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2021, 37(6): 78-84. |
| [Yang Xiuping, Wang Like, Li Yabing, et al. Review and prospects of resilient city theory[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2021, 37(6): 78-84.] | |
| [25] | 韩自强, 刘杰, 田万方. 城市韧性的测量指标: 基于国际文献的系统综述[J]. 广州大学学报(社会科学版), 2022, 21(6): 131-144. |
| [Han Ziqiang, Liu Jie, Tian Wanfang. Measurements of urban resilience: A systematic review of international literature[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Social Science Edition), 2022, 21(6): 131-144.] | |
| [26] | 焦柳丹, 邓佳丽, 吴雅, 等. 基于PSR+云模型的城市韧性水平评价研究[J]. 生态经济, 2022, 38(5): 114-120. |
| [Jiao Liudan, Deng Jiali, Wu Ya, et al. Evaluation of urban resilience based on PSR+ cloud model[J]. Ecological Economy, 2022, 38(5): 114-120.] | |
| [27] | 王国萍, 闵庆文, 丁陆彬, 等. 基于PSR模型的国家公园综合灾害风险评估指标体系构建[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(22): 8232-8244. |
| [Wang Guoping, Min Qingwen, Ding Lubin, et al. Comprehensive disaster risk assessment index system for national parks based on the PSR model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(22): 8232-8244.] | |
| [28] |
宁静, 朱冉, 张馨元, 等. 内蒙古区县城市韧性评价与分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(7): 1217-1226.
doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.537 |
|
[Ning Jing, Zhu Ran, Zhang Xinyuan, et al. Evaluation and analysis of urban resilience of districts and counties in Inner Mongolia[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(7): 1217-1226.]
doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.537 |
|
| [29] | 杨桐彬, 朱英明, 姚启峰. 中国城市群经济韧性的地区差异、分布动态与空间收敛[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2022, 37(7): 45-60. |
| [Yang Tongbin, Zhu Yingming, Yao Qifeng. Regional differences, distribution dynamics and spatial convergence of economic resilience in Chinese urban agglomerations[J]. Journal of Statistics and Information, 2022, 37(7): 45-60.] |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 68
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 193
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||

