- 2025年5月10日 星期六
干旱区地理 ›› 2021, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 471-483.doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000–6060.2021.02.18
收稿日期:2020-04-20
修回日期:2020-07-24
出版日期:2021-03-25
发布日期:2021-04-14
通讯作者:
杨艳敏
作者简介:俞琳飞(1995-),男,博士研究生,主要从事遥感水文研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
YU Linfei1,2( ),YANG Yonghui1,YANG Yanmin1(
),YANG Yonghui1,YANG Yanmin1( )
)
Received:2020-04-20
Revised:2020-07-24
Online:2021-03-25
Published:2021-04-14
Contact:
Yanmin YANG
摘要:
卫星遥感观测技术的不断发展,为全球降水准确定量观测提供新的手段,应用卫星降水产品的前提是进行地区的适用性评价。为了解卫星降水产品评价的研究现状和热点,以Web of Science数据库核心合集中1998—2020年752篇文献作为研究对象,利用文献计量和网络分析的方法剖析卫星降水产品评价研究的演变趋势、合作关系和研究热点,以此来了解该领域的前沿进展。结果表明:该领域的研究论文发文量和引文量不断增长,且2015年开始高被引论文显著增多。美国、中国和德国是该领域的主要发文国家,美国和中国占到世界总发文量的76.2%,中国科学院是全球该领域发文量最大的学术机构,占到发文总量的11.6%。基于卫星降水数据在复杂地形区的多时空尺度评价、极端降水事件分析、大尺度干旱评价等是该领域的主要研究方向;典型的研究区包括青藏高原、拉普拉塔流域等。基于卫星降水数据在无资料地区的水文过程模拟、结合人工智能方法进行气候变化模拟、气象预报和预测等是该领域未来研究方向和热点。
俞琳飞,杨永辉,杨艳敏. 卫星降水产品评价研究的演进脉络与前沿进展[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(2): 471-483.
YU Linfei,YANG Yonghui,YANG Yanmin. Evolution and frontier development of research on evaluation of satellite precipitation product[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(2): 471-483.
表1
全球发文量前10的国家"
| 排名 | 国家/地区 | 记录 | 发文量占比/% | h指数 | 每项平均被引用次数 | 被引次总计 | 去除自引 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 美国(USA) | 336 | 44.68 | 61 | 38.37 | 12893 | 11610 |
| 2 | 中国(China) | 237 | 31.52 | 33 | 17.39 | 4122 | 2981 |
| 3 | 德国(Germany) | 59 | 7.85 | 23 | 24.32 | 1435 | 1396 |
| 4 | 英国(England) | 54 | 7.18 | 26 | 71.28 | 3849 | 3820 |
| 5 | 意大利(Italy) | 48 | 6.38 | 20 | 27.75 | 1332 | 1293 |
| 6 | 印度(India) | 46 | 6.12 | 15 | 13.72 | 631 | 574 |
| 7 | 法国(France) | 44 | 5.85 | 18 | 32.73 | 1440 | 1409 |
| 8 | 荷兰(Netherlands) | 39 | 5.19 | 20 | 31.54 | 1230 | 1194 |
| 9 | 澳大利亚(Australia) | 31 | 4.12 | 15 | 33.35 | 1034 | 1021 |
| 10 | 日本(Japan) | 26 | 3.46 | 13 | 35.42 | 921 | 914 |
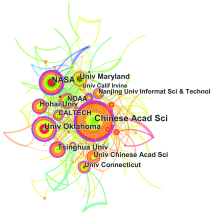
图4
研究机构合作共现图谱 注:节点大小代表研究机构的发文量,节点间连线代表机构间的合作。Chinses Acad Sci:中国科学院;NASA:美国国家航天航空局;Univ Oklahoma:俄克拉荷马大学;Univ Maryland:马里兰大学;Tsinghua Univ:清华大学;Univ Chinses Acad Sci:中国科学院大学;NOAA:美国国海洋和大气管理局;Univ Connecticut:康涅狄格大学;CALTECH:加州理工学院;Hohai Univ:河海大学;Univ Calif Irvine:加利福尼亚州大学尔湾分校;Nanjing Univ Informat Sci & Technol:南京信息工程大学。"

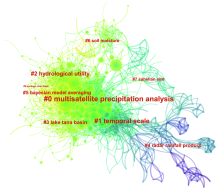
图6
卫星降水产品评价文献共被引分析图谱 注:节点大小代表文献共被引频次,红色字体为共被引网络的聚类标签。数字编号代表聚类排序。#0 multisatellite precipitation analysis:多卫星降水分析;#1 temporal scale:时间尺度;#2 hydrological utility:水文应用;#3 lake tana basin:塔纳湖流域;#4 radar rainfall product:雷达降水产品;#5 bayesian model averaging:贝叶斯模型平均;#6 soil moisture:土壤湿度;#7 sahelian site:萨赫勒地区站点;#9 santiago river basin:圣地亚哥流域。"

表2
Web of Science 数据库卫星降水产品评价文献共被引分析"
| 频次 | 第一作者 | 发表年份 | 题目 | 期刊 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 137 | Huffman G J | 2007 | The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales | Journal of Hydrometeorology |
| 136 | Hou A Y | 2014 | The global precipitation measurement mission | Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society |
| 91 | Tang G Q | 2016 | Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales | Journal of Hydrology |
| 90 | Ashouri H | 2015 | PERSIANN-CDR: Daily precipitation climate data record from multisatellite observations for hydrological and climate studies | Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society |
| 79 | Dee D P | 2011 | The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system | Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society |
| 75 | Behrangi A | 2011 | Hydrological evaluation of satellite precipitation products over a mid-size basin | Journal of Hydrology |
| 71 | Ebert E E | 2007 | Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models | Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society |
| 71 | Xue X W | 2013 | Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based multi-satellite precipitation analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? | Journal of Hydrology |
| 66 | Su F G | 2008 | Evaluation of TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin | Journal of Hydrometeorology |
| 63 | Hirpa F A | 2010 | Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over very complex terrain in Ethiopia | Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology |

图8
卫星降水产品评价关键词共现时间线 注:节点大小代表关键词的共现频率;红色字为聚类标签;水平线长代表该类关键词的持续时间;顶部数字为各时间切片的末尾年份。#0 multisatellite precipitation analysis:多卫星降水分析;#1 summer precipitation variation:夏季降水变化;#2 performance evaluation:表现评价;#3 spatio-temporal evaluation:时空评价;#4 Tibetan Plateau:青藏高原;#5 drought indice:干旱指数;#6:leaf area index:叶面积指数;#7 La Plata Basin:拉普拉塔流域;#8 model-based bayesian technique:基于模型的贝叶斯方法。"
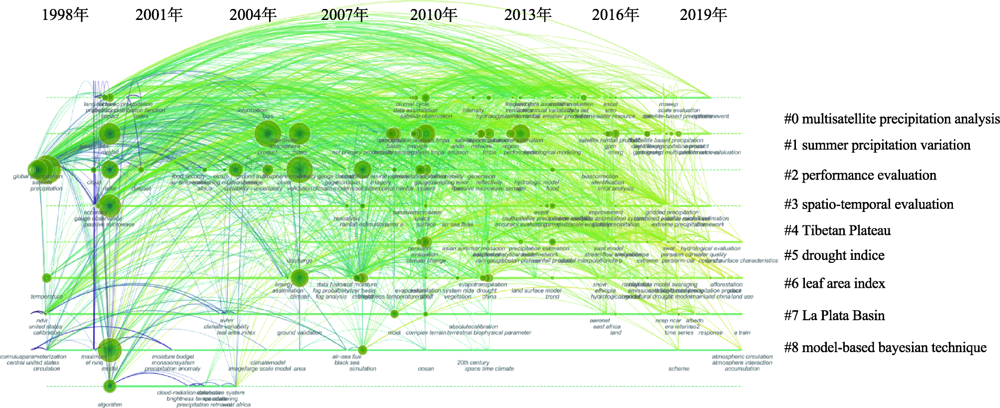
表3
关键词聚类"
| 聚类编号 | 聚类内节点数 | 平均年份 | 聚类标签 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 64 | 2012 | west Africa; hydrolgical applications; several rainfall products; high-resolution gauge networks; Colorado flash flood; southeastern south America; using high-resolution numerical weather forecasts; springtime precipitation; using gauge observations | TRMM; drought monitoring; Jiangsu; China; precipitation data; uncertainty quantification; different seasons; spatial evaluation; global climate models; water vapor flux |
| 1 | 61 | 2012 | precipitation products; complex mountainous terrain; water resources perspective; Pakistan; precipitation; satellite-derived agro-climate variables; states; northern great plains; dynamic Bayesian model | China; Yellow River; reliability; gridded precipitation products; central Mediterranean; satellite-derived global precipitation estimates; spatial evaluation; dynamic Bayesian model; water resources perspective; precipitation datasets |
| 2 | 58 | 2007 | evaluation; complex mountainous terrain; precipitation products; water resources perspective; trend analysis; microwave estimates; rain estimation; using forward-adjusted advection; west Africa; extreme events | performance evaluation; seasonal signatures; hydrologic predictability; merged satellite rainfall products; evaluation; using rain gauge measurements; TRMM ground-validation radar-rain errors; complex mountainous terrain; precipitation products; water resources perspective |
| 3 | 56 | 2013 | evaluation; central Asia; precipitation data sets; benchmarking high-resolution global satellite rainfall products; radar; PERSIANN system; tropical rainfall; satellite-based estimates; Pakistan; algorithm | China; Yellow River; reliability; gridded precipitation products; assessment; mainland china; high-resolution satellite precipitation products; precipitation trends; analysing ground reference uncertainty; Australian snowpack |
| 4 | 50 | 2015 | evaluation; China; TRMM; hydrological application; NCEP-CFSR; precipitation estimates; humid regions; IMERG satellite precipitation products; ground-based data; correction | basin; hydrological evaluation; Ethiopia; air temperature datasets; using swat; open-access precipitation; reanalysis precipitation products; precipitation datasets; mountainous basins; multiple satellite precipitation products |
| 5 | 50 | 2012 | evaluation; China; TMPA satellite precipitation product; hydrologic validation; Pearl River; water balance perspective; evapotranspiration; machine learning techniques; sensitivity testing; considering global warming | drought indices; long-term satellite-based precipitation products; applicability; considering global warming; integration; mainland China; bottom-up satellite precipitation products; machine learning techniques; satellite soil moisture; downscaling |
| 6 | 40 | 2011 | evaluation; cloud; cloud-aerosol lidar; vertical structure; infrared pathfinder satellite observations; reanalyses; forest; evaluating PERSIANN-CCS; NOAA AVHRR satellite data | RHESSys model; climate change; watershed hydro-ecology; effects; Seolma-cheon catchment; forest; different spatial resolution; yield variability; plot; soybean crop coverage estimation |
| 7 | 33 | 2004 | cloud; atmospheric radiation measurement march; midlatitude; simulations; cloud-resolving models; frontal clouds; intensive operational period; precipitation data sets; observations; temperature | river discharges; air-sea fluxes; Danube; Bosphorus; black sea; focus; methods; products; reintroduction programmes |
| 8 | 11 | 2003 | evaluation; precipitation; real-time rainfall product; comparison; soil moisture; high-resolution tropical weather forecasts; storm scales; using MODIS gross primary productivity; millimeter-wave observations; gridded precipitation datasets | using MODIS gross primary productivity; vegetation activities; evapotranspiration products; climatological perspectives; Korean regional flux network site; evaluating ecohydrological impacts; millimeter-wave observations; west Africa; high-resolution tropical weather forecasts; storm scales |
| [1] | Xu R, Tian F Q, Yang L, et al. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017,122:1-15. |
| [2] | Zambrano-bigiarini M, Nauditt A, Birkel C. Temporal and spatial evaluation of satellite-based rainfall estimates across the complex topographical and climatic gradients of Chile[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 2017,21:1295-1320. |
| [3] | Howat I M, Tulaczyk S, Rhodes P. A precipitation-dominated, mid-latitude glacier system: Mount Shasta, California[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2007,28(1):85-98. |
| [4] | Keller S, Atzl A. Mapping natural hazard impacts on road infrastructure: The extreme precipitation in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, June 2013[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 2014,5(3):227-241. |
| [5] | Mo K L, Chen Q W, Chen C, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of correlation between vegetation cover and precipitation in an arid mountain-oasis river basin in northwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019,574:138-147. |
| [6] | Hui-mean F, Yusop Z, Yusof F. Drought analysis and water resource availability using standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2018,201:102-115. |
| [7] | Trenbrth K E, Smith L, Qian T, et al. Estimates of the global water budget and its annual cycle using observational and model data[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2007,8(4):758-769. |
| [8] | Skliris N, Marsh R, Josey S A, et al. Salinity changes in the world ocean since 1950 in relation to changing surface freshwater fluxes[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2014,43(3-4):709-736. |
| [9] | Zhang Y J, Duo L, Pang Y Z, et al. Modern pollen assemblages and their relationships to vegetation and climate in the Lhasa Valley, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2018,467(Part B):210-221. |
| [10] | 唐国强, 万玮, 曾子悦, 等. 全球降水测量(GPM)计划及其最新进展综述[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2015,30(4):607-615. |
| [ Tang Guoqiang, Wan Wei, Zeng Ziyue, et al. An overview of the global precipitation measurement (gpm) mission and its latest development[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2015,30(4):607-615. ] | |
| [11] | Baroentti A, Acquaotta F, Fratianni S. Rainfall variability from a dense rain gauge network in north-west Italy[J]. Climate Research, 2018,75(3):201-213. |
| [12] | Foehn A, Hernánez G A, Schaefli B, et al. Spatial interpolation of precipitation from multiple rain gauge networks and weather radar data for operational applications in Alpine catchments[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018,563:1092-1110. |
| [13] | Tang G Q, Behrangi A, Long D, et al. Accounting for spatiotemporal errors of gauges: A critical step to evaluate gridded precipitation products[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018,559:294-306. |
| [14] | Hou A Y, Kakar R K, Neeck S, et al. The global precipitation measurement mission[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2014,95(5):701-722. |
| [15] | 马自强. 青藏高原地区卫星降水时空降尺度研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. |
| [ Ma Ziqiang. Downscaling satellite-based precipitation estimates over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau at different temporal scales[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. ] | |
| [16] | Huffman G J, Adler R F, Bolvin D T, et al. The TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2007,8(1):38-55. |
| [17] | Huffman G J, Adler R F, Arkin P, et al. Improving the global precipitation record: GPCP Version 2.1[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009,36(17):153-159. |
| [18] | Kummerow C D, Barnes W, Kozu T, et al. The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package[J]. Journal Atmospheric Ocean Technology, 1998,15:809-917. |
| [19] | Tomoo U, Kazishi S, Takuji K, et al. A Kalman filter approach to the global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) from combined passive microwave and infrared radiometric data[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 2009,87A:137-151. |
| [20] | Hong Y, Chen S, Xue X, et al. Multiscale hydrologic remote sensing: Perspectives and applications[M]. CRC Press, 2012, 371-386. |
| [21] |
Falags M E, Pitsouni E I, Malietzis G A, et al. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and weaknesses[J]. Faseb Journal, 2008,22(2):338-342.
doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9492LSF pmid: 17884971 |
| [22] | De Bakker F G A, Groenewegen P, Hond F D. A bibliometric analysis of 30 years of research and theory on corporate social responsibility and corporate social performance[J]. Business & Society, 2005,44(3):283-317. |
| [23] | 赵蓉英, 许丽敏. 文献计量学发展演进与研究前沿的知识图谱探析[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2010(5):62-70. |
| [ Zhao Rongying, Xu Limin. The knowledge map of the evolution and research frontiers of bibiometrics[J]. Journal of Library Science in China, 2010(5):62-70. ] | |
| [24] | Chen C M. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 2006,57(3):359-377. |
| [25] | Chen C M. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004,101(Suppl. 1):5303-5310. |
| [26] | 陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究, 2015. 33(2):242-253. |
| [ Chen Yue, Chen Chaomei, Liu Zeyuan, et al. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains[J]. Studies in Science of Science, 2015,33(2):242-253. ] | |
| [27] | 李杰, 陈超美. CiteSpace: 科技文本挖掘及可视化[M]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学出版社, 2016. |
| [ Li Jie, Chen Chaomei. CiteSpace: Text mining and visualization in scientific literature[M]. Beijing: Capital University of Economic and Business Press, 2016. ] | |
| [28] | White H, Mccain K. Visualizing a discipline: An author co-citation analysis of information science[J]. Journal of the Association for Information Science & Technology, 2010,49(4):327-355. |
| [29] | Nerini D, Zulkafli Z, Wang L P, et al. A comparative analysis of TRMM-rain gauge data merging techniques at the daily time scale for distributed rainfall-runoff modeling applications[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2015,16(5):2153-2168. |
| [30] | Munier S, Aires F, Schlaffer S, et al. Combining data sets of satellite-retrieved products for basin-scale water balance study: Evaluation on the Mississippi Basin and closure correction model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 2014,119(21):12100-12116. |
| [31] | Tan M L, Chua V P, Tan K C, et al. Evaluation of TMPA 3B43 and NCEP-CFSR precipitation products in drought monitoring over Singapore[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018,39(8):2089-2104. |
| [32] | Tang G Q, Ma Y Z, Long D. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016,533:152-167. |
| [33] | Ashouri H, Hsu K L, Sorooshian S, et al. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily precipitation climate data record from multisatellite observations for hydrological and climate studies[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2015,96(1):69-83. |
| [34] | Dee D P, Uppala S M, Simmons A J, et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2011,137:553-597. |
| [35] | Behrangi A, Khakbaz B, Jaw T C, et al. Hydrologic evaluation of satellite precipitation products over a mid-size basin[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011,397(3-4):225-237. |
| [36] | Ebert E E, Janowiak J E, Kidd C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2007,88(1):47-64. |
| [37] | Xue X, Hong Y, Limaye A S, et al. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based multi-satellite precipitation analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins?[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013,499:91-99. |
| [38] | Su F, Hong Y, Lettenmaier D P. Evaluation of TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2008,9(4):622-640. |
| [39] | Hirpa F A, Gebrebremichael M, Hopson O T. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over very complex terrain in Ethiopia[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology & Climatology, 2010,49(5):1044-1051. |
| [40] | 王云, 马丽, 刘毅. 城镇化研究进展与趋势——基于CiteSpace和HistCite的图谱量化分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018,37(2):239-254. |
| [ Wang Yun, Ma Li, Liu Yi. Progress and trend analysis of urbanization research: Visualized quantitative study based on CiteSpace and HistCite[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018,37(2):239-254. ] | |
| [41] | 郭瑞芳, 刘元波. 多传感器联合反演高分辨率降水方法综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015,30(8):891-903. |
| [ Guo Ruifang, Liu Yuanbo. Multi-satellite retrieval of high resolution precipitation: An overview[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015,30(8):891-903. ] | |
| [42] | 唐国强, 龙笛, 万玮, 等. 全球水遥感技术及其应用研究的综述与展望[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2015(45):1013-1023. |
| [ Tang Guoqiang, Long Di, Wan Wei, et al. An overview and outlook of global water remote sensing technology and applications[J]. Scienta Sinica Technology, 2015(45):1013-1023. ] | |
| [43] | 肖柳斯, 张阿思, 闵超, 等. GPM卫星降水产品在台风极端降水过程的误差评估[J]. 高原气象, 2019,38(5):993-1003. |
| [ Xiao Liusi, Zhang Asi, Min Chao, et al. Evaluation of GPM satellite-based precipitation estimates during three tropical-related extreme rainfall events[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2019,38(5):993-1003. ] | |
| [44] | 廖荣伟, 张冬斌, 沈艳. 6种卫星降水产品在中国区域的精度特征评估[J]. 气象, 2015,41(8):970-979. |
| [ Liao Rongwei, Zhang Dongbin, Shen Yan. Validation of six satellite-derived rainfall estimates over China[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2015,41(8):970-979. ] | |
| [45] | 潘旸, 宇婧婧, 廖捷, 等. 地面和卫星降水产品对台风莫拉克降水监测能力的对比分析[J]. 气象, 2011,37(5):564-570. |
| [ Pan Yang, Yu Jingjing, Liao Jie, et al, Assessment of the rainfall monitoring of Typhoon Morakot by ground-gauged and satellite precipitation products[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011,37(5):564-570. ] | |
| [46] | Argueso D, Di Luca A, Evans J P. Precipitation over urban areas in the western maritime continent using a convection-permitting model[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016,47(3-4):1143-1159. |
| [47] | Tesfaye M, Botaj J, Sivakumar V, et al. Evaluation of regional climatic model simulated aerosol optical properties over South Africa using ground-based and satellite observations[J]. ISRN Atmospheric Sciences, 2013,237483, doi: 10.1155/2013/237483. |
| [48] | Zambrano F, Wardlow B, Tadesse T, et al. Evaluating satellite-derived long-term historical precipitation datasets for drought monitoring in Chile[C]// Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems & Hydrology XVIII. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2017, 26-42. |
| [49] | Sahoo A K, Sheffield J, Pan M, et al. Evaluation of the tropical rainfall measuring mission multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) for assessment of large-scale meteorological drought[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015,159:181-193. |
| [50] |
Ryo M, Valeriano O C S, Kanae S, et al. Temporal downscaling of daily gauged precipitation by application of a satellite product for flood simulation in a poorly gauged basin and its evaluation with multiple regression analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2014,15(2):563-580.
doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-13-052.1 |
| [51] |
Peng B, Shi J, Ni-meister W, et al. Evaluation of TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) products and their potential hydrological application at an arid and semiarid basin in China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014,7(9):3915-3930.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320756 |
| [52] | Wang Z, Zhong R, Lai C, et al. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017,196:151-163. |
| [53] | Jiang S, Ren L, Hong Y, et al. Improvement of multi-satellite real-time precipitation products for ensemble streamflow simulation in a middle latitude basin in south China[J]. Water Resources Management, 2014,28(8):2259-2278. |
| [54] | Wei H, Li J, Liang T. Study on the estimation of precipitation resources for rainwater harvesting agriculture in semi-arid land of China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2005,71(1):33-45. |
| [55] | Kukal M S, Suat I. Spatial and temporal changes in maize and soybean grain yield, precipitation use efficiency, and crop water productivity in the U. S. great plains[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2017,60(4):1189-1208. |
| [1] | 张昊, 韩增林, 乔国荣, 王辉, 王宏业, 段冶. 黄河流域城市间旅游经济联系格局及影响因素研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(8): 1344-1354. |
| [2] | 卢北, 曾俊伟, 钱勇生, 魏谞婷, 杨民安, 李海军. 兰州市主城区路网形态对城市活力的影响分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(8): 1333-1343. |
| [3] | 李嘉会,吴金华,王祯,白雨霞. 黄土丘陵沟壑区农村居民点发展类型识别——以吴起县为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(3): 397-406. |
| [4] | 王志强, 姜文桓, 卢诗月. 基于生态网络分析的新疆“水-能-碳”耦合系统特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(12): 2005-2016. |
| [5] | 李南, 李晓东, 刘想, 刘柏伶. 新疆区域经济联系网络时空格局演变[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(6): 1978-1987. |
| [6] | 周春山,陈楷锐,白克拉木·孜克利亚. 基于科学知识图谱的干旱区城镇化文献计量分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(2): 578-592. |
| [7] | 叶珊珊,曹明明,胡胜. 关中平原城市群经济联系网络结构演变及对经济增长影响研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(1): 277-286. |
| [8] | 高玉祥,董晓峰,梁颖. 基于GIS的宁夏路网空间特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(1): 268-276. |
| [9] | 王松茂, 徐宣国, 马江涛, 王艳威. 新疆旅游经济网络特征的时空演变研究——基于修正的引力模型及社会网络分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(2): 458-465. |
| [10] | 王涛, 王晴晴, 赵丹, 童超. 资源型地区产业多元化问题研究——以山西省为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(5): 1221-1228. |
| [11] | 孔令章, 李晓东, 白 洋, 江 瞳. 长距离高铁对沿线城市旅游经济联系的空间影响及角色分析——以兰新高铁为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(3): 681-688. |
| [12] | 员学锋, 邵雅静, 侯瑞, 卫新东. 土地污染文献定量分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(4): 824-830. |
| [13] | 张雪妮,吕光辉,赵晓英,马玉,朱修逸,郭振洁. 1990-2012年国内有关中亚研究的文献计量分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2014, 37(4): 857-864. |
| [14] | 王彦,田长彦. 基于Web of Science的盐生植物研究文献计量评价[J]. 干旱区地理, 2013, 36(3): 562-570. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 92
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 393
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||
