干旱区地理 ›› 2023, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1024-1037.doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.394 cstr: 32274.14.ALG2022394
• 区域发展 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-08-11
修回日期:2022-10-26
出版日期:2023-06-25
发布日期:2023-07-24
作者简介:王一丹(1998-),女,硕士研究生,主要从事城市全球化等方面的研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
WANG Yidan1( ),YANG Yongchun1,2(
),YANG Yongchun1,2( ),LIU Qing3,LU Zhongmingnan4,HE Yao1
),LIU Qing3,LU Zhongmingnan4,HE Yao1
Received:2022-08-11
Revised:2022-10-26
Published:2023-06-25
Online:2023-07-24
摘要:
以敦煌市为例,从居民观念认同和感知的视角构建结构方程模型,探讨敦煌市城市全球化的影响因子和作用路径,并结合改革开放以来敦煌市的全球化表现,分析文化旅游导向的中国内陆城市的“反向”全球化路径。结果表明:(1) 本地居民全球化观念认同正向促进了敦煌市城市全球化过程。对外交往与合作对敦煌市城市全球化发展的推动是通过提升城市文化旅游资源全球影响力间接实现的,机构交流合作与学术讨论可以显著提升城市旅游知名度。城市景观与国际接轨可以促进敦煌市日益融入国际旅游网络。(2) 敦煌市城市转型与全球化发展可分为3个阶段,第一阶段在境外游客参观访问产生的市场需求推动下,实现由传统农业县向文化旅游城市转型;第二阶段形成了以文化旅游产业为支柱的城市经济发展模式,并加速完善和提升城市基础设施和服务设施;第三阶段由现代文化旅游城市向“国际交流中心”“国际一流旅游目的地”转型,持续深化文旅产业融合,加强全球目标市场开拓。(3) 受市场力量驱动和政府宏观政策调控影响,敦煌市旅游要素时空演化具有明显的阶段性、不平衡性和非均衡性。研究结果可为此类城市突破“路径锁定”,科学制定全球化战略提供参考,是关系到我国崛起与全方位开放的重大科学问题。
王一丹, 杨永春, 刘清, 陆仲明楠, 何瑶. 基于居民感知的敦煌市旅游全球化路径研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(6): 1024-1037.
WANG Yidan, YANG Yongchun, LIU Qing, LU Zhongmingnan, HE Yao. Globalization path of cultural tourism cities based on residents’ perception: A case of Dunhuang City, China[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(6): 1024-1037.
图1
文化旅游型城市全球化形象居民感知概念模型 注:H1a为具有全球化观念认同的本地居民能够更为灵敏的感知敦煌市文化交流全球化;H1b为具有全球化观念认同的本地居民能够更为灵敏的感知敦煌市品牌全球化;H1c为具有全球化观念认同的本地居民能够更为灵敏的感知敦煌市全球化形象;H2a为本地居民认为敦煌市交通与通信全球化在促进敦煌市文化交流全球化方面具有显著作用;H2b为本地居民认为敦煌市交通与通信全球化在促进敦煌市品牌全球化方面具有显著作用;H3a为本地居民认为敦煌市景观全球化在促进敦煌市文化交流全球化方面具有显著作用;H3b为本地居民认为敦煌市景观全球化在促进敦煌市品牌全球化方面具有显著作用;H4a为本地居民认为敦煌市外语环境国际化在促进敦煌市文化交流全球化方面具有显著作用;H4b为本地居民认为敦煌市外语环境全球化在促进敦煌市品牌全球化方面具有显著作用;H4c为本地居民认为敦煌市外语环境全球化在促进敦煌市城市全球化方面具有显著作用;H5a为本地居民认为敦煌市文化交流全球化在促进敦煌市品牌全球化方面具有显著作用;H5b为本地居民认为敦煌市文化交流全球化在促进敦煌市城市全球化方面具有显著作用;H6a为本地居民认为旅游城市品牌全球化在促进敦煌市品牌全球化方面具有显著作用;H6b为本地居民认为旅游城市品牌全球化在促进敦煌市城市全球化方面具有显著作用。下同。"
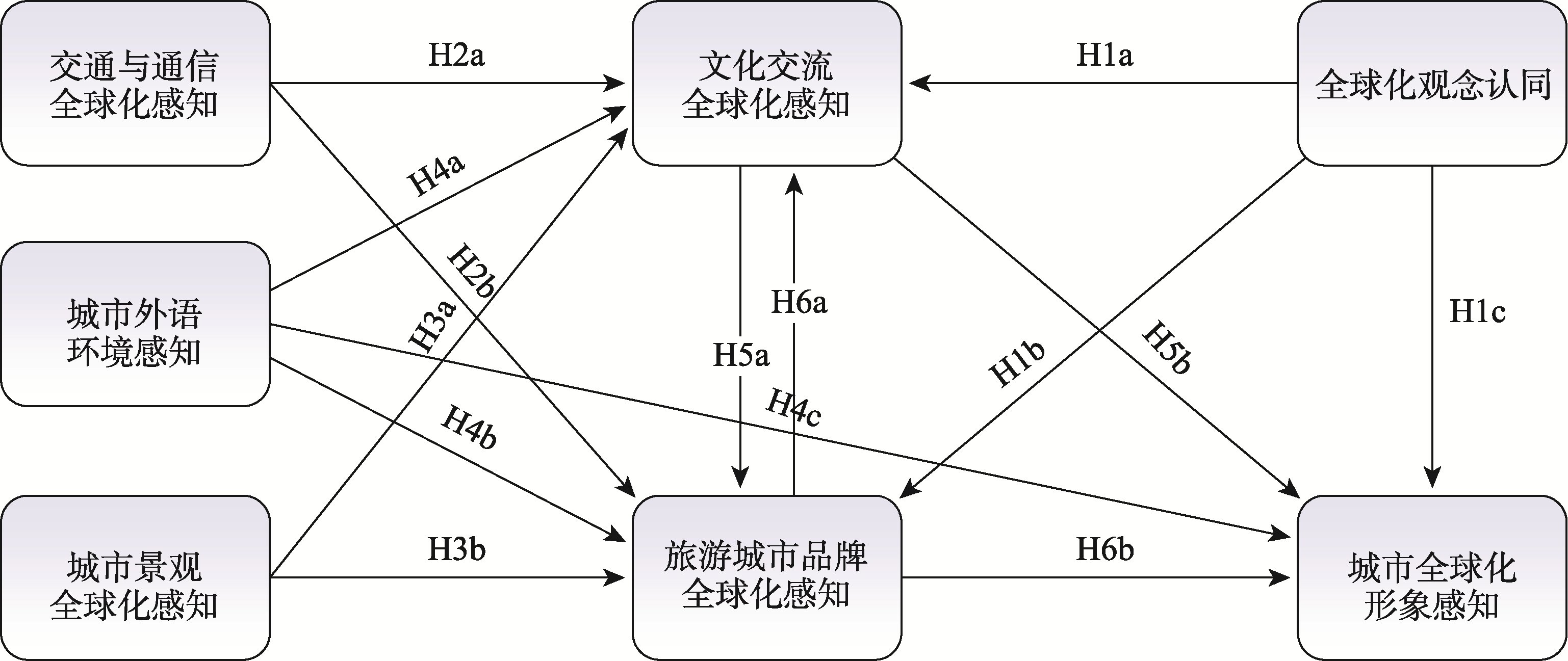
表1
概念测量"
| 概念 | 编码 | 观测变量 | 参考来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 全球化观念认同 (GI) | GI1 | 我与世界联系紧密 | Joseph等[ |
| GI2 | 我乐于接受和学习外来文化、思想观念与生活方式 | ||
| GI3 | 我对全球世界有很强的依恋情感 | ||
| GI4 | 全球化对敦煌市旅游发展前景很重要 | ||
| 城市全球化形象感知 (PGCI) | PGCI1 | 敦煌市正在全球化 | Zhu等[ |
| PGCI2 | 敦煌市在各历史时期都承担对外交往的重要国际职能 | ||
| PGCI3 | 敦煌市的旅游接待水平越来越全球化 | ||
| PGCI4 | 敦煌市文化的全球影响力越来越强 | ||
| 文化交流全球化感知 (PCG) | PCG1 | 全球范围内研究学习“敦煌学”的机构、学者众多 | 余国扬[ |
| PCG2 | 全球发行的有关敦煌学的论文、专著众多 | ||
| PCG3 | 敦煌市研究机构组织国际文化出访与来访批次日益增多 | ||
| PCG4 | 以敦煌市文化为题材的影视作品、歌舞剧、艺术等日益走向世界 | ||
| PCG5 | 敦煌市中西方文化交流较深,既影响着全球宗教文化,又塑造了地方浓厚的礼佛之风 | ||
| PCG6 | 敦煌学和宗教文化可以在全球的宗教信仰者引起共鸣 | ||
| 交通与通信全球化感知 (PTCG) | PTCG1 | 敦煌市国际航空港建设日益完备,国际航空旅客吞吐量日益增大 | 刘卫东[ |
| PTCG2 | 敦煌市国际定期直飞航线覆盖区域越来越广 | ||
| PTCG3 | 敦煌市国际互联网出口带宽覆盖范围越来越广,互联网用户普及率日益提高 | ||
| 城市景观全球化感知 (PULG) | PULG1 | 旅游建设促进了敦煌市的建筑形式国际化发展 | 卢松等[ |
| PULG2 | 敦煌市星级宾馆、饭店、国际旅行社日益增多 | ||
| PULG3 | 敦煌市的城市规划、建设、景区开发越来越面向全球化 | ||
| PULG4 | 敦煌市的国际会展中心、大剧院、博物馆文化设施建设越来越与国际接轨 | ||
| 旅游城市品牌全球化感知(PTCBG) | PTCBG1 | 敦煌市承办的国际节事、会议增多,全球旅游知名度提高 | 袁玲燕等[ |
| PTCBG2 | 敦煌市莫高窟的佛教文化旅游具有全球影响力 | ||
| PTCBG3 | 敦煌市政府、文化研究机构越来越重视敦煌旅游品牌的全球营销与宣传 | ||
| PTCBG4 | 敦煌市的文创产品、地方美食、风俗文化、特色节庆对国际游客具有吸引力 | ||
| 城市外语环境感知 (PFLUE) | PFLUE1 | 敦煌市会说外语或学习外语的人数越来越多 | 徐茗等[ |
| PFLUE2 | 敦煌市的外文媒体、营销网站、旅游介绍、外文出版物日益增多 | ||
| PFLUE3 | 敦煌市的外文公共标识、旅游景区标识越来越多 | ||
| PFLUE4 | 地方当局对居民/从业人员英语学习的推广力度和重视程度越来越大 |
表4
标准化后敦煌市居民城市全球化形象感知结构方程模型潜变量间的连锁效应"
| 效应类型 | 路径 | 标准化路径系数 |
|---|---|---|
| 间接效应 | 交通与通信全球化→文化交流全球→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.04 |
| 城市景观全球化→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.20 | |
| 城市景观全球化→文化交流全球化→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.05 | |
| 城市外语环境→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市形象全球化 | 0.07 | |
| 城市外语环境→文化交流全球化→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市形象全球化 | 0.02 | |
| 全球化观念认同→文化交流全球化→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.02 | |
| 文化交流全球化→旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.14 | |
| 直接效应 | 旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.33 |
| 总效应 | 交通与通信全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.04 |
| 城市景观全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.25 | |
| 城市外语环境→城市形象全球化 | 0.09 | |
| 全球化观念认同→城市全球化形象 | 0.41 | |
| 文化交流全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.14 | |
| 旅游城市品牌全球化→城市全球化形象 | 0.33 |
| [1] |
Herbert C W, Murray M J. Building from scratch: New cities, privatized urbanism and the spatial restructuring of Johannesburg after apartheid[J]. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 2015, 39: 471-494.
doi: 10.1111/1468-2427.12180 |
| [2] |
Watson V. African urban fantasies: Dreams or nightmares?[J]. Environment and Urbanization, 2014, 26(1): 215-231.
doi: 10.1177/0956247813513705 |
| [3] |
Yao C, Richard L. China’s hybrid global city region pathway: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Cities, 2018, 77: 81-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2018.01.015 |
| [4] |
Ilya C, Daniel B. Multiple pathways to global city formation: A functional approach and review of recent evidence in China[J]. Cities, 2013, 35: 181-189.
doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2013.05.008 |
| [5] |
Wei Y D, Leung C K. Development zones, foreign investment, and global city formation in Shanghai[J]. Growth and Change, 2005, 36: 16-40.
doi: 10.1111/grow.2005.36.issue-1 |
| [6] |
Gibb M, Cape T. A secondary global city in a developing country[J]. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy, 2007, 25(4): 537-552.
doi: 10.1068/c6p |
| [7] |
康江江, 徐伟, 宁越敏. 基于地方化、城市化和全球化制造业空间集聚分析- -以长三角区域为例[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(10): 1773-1782.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.10.009 |
|
[Kang Jiangjiang, Xu Wei, Ning Yuemin. Dynamic regional manufacturing agglomeration in the Yangtze River Delta region[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 1773-1782.]
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.10.009 |
|
| [8] | 李正图, 姚清铁. 经济全球化、城市网络层级与全球城市演进[J]. 华东师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2019, 51(5): 67-78, 237-238. |
| [Li Zhengtu, Yao Qingtie. Economic globalization, city network and the development of global cities[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2019, 51(5): 67-78, 237-238.] | |
| [9] | 屠启宇. 21世纪全球城市理论与实践的迭代[J]. 城市规划学刊, 2018(1): 41-49. |
| [Tu Qiyu. On the evolution of global city theory and practices[J]. Urban Planning Forum, 2018(1): 41-49.] | |
| [10] |
贺灿飞, 胡绪千. 1978年改革开放以来中国工业地理格局演变[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(10): 1962-1979.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201910002 |
|
[He Canfei, Hu Xuqian. Evolution of Chinese industrial geography since reform and opening-up[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(10): 1962-1979.]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201910002 |
|
| [11] | 程惠芳. 经济全球化与国际直接投资发展路径探讨[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2002(3): 3-9. |
| [Cheng Huifang. The study of economic globalization and the development path to foreign direct investment[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2002(3): 3-9.] | |
| [12] | 杨丹辉. 全球化、服务外包与后起国家产业升级路径的变化: 印度的经验及其启示[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2010(4): 160-165. |
| [Yang Danhui. Globalization, service outsourcing and the changing path of industrial upgrading in latecomer countries: India’s experience and its implications[J]. Comparative Economic and Social Systems, 2010(4): 160-165.] | |
| [13] | 张懿玮, 高维和. 从服务型城市到全球城市的逻辑机理和实现路径[J]. 北京社会科学, 2021(7): 63-75. |
| [Zhang Yiwei, Gao Weihe. From service-oriented city to global city: Logical mechanism and realization path[J]. Social Sciences of Beijing, 2021(7): 63-75.] | |
| [14] |
Li F X, Zhang G J. Border resident perceptions of sanctions and tourism: A case study of North Korea[J]. Tourism Management Perspectives, 2021, 38(14): 100821, doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100821.
doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100821 |
| [15] |
Tovar B, Espino R F, Pino L D. Residents’ perceptions and attitudes towards the cruise tourism impact in Gran Canaria[J]. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 2020, 45(7): 100586, doi: 10.1016/j.rtbm.2020.100586.
doi: 10.1016/j.rtbm.2020.100586 |
| [16] |
Sung H, Jung U. Radiation risk perception and its associated factors among residents living near nuclear power plants: A nationwide survey in Korea[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2022, 54(4): 1295-1300.
doi: 10.1016/j.net.2021.10.017 |
| [17] |
Hateftabar F, Chapuis J M. How resident perception of economic crisis influences their perception of tourism[J]. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 2020, 43: 157-168.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.02.009 |
| [18] |
Shama N, Xu H. Infrastructure-driven development and sustainable development goals: Subjective analysis of residents’ perception[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 294: 112931, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112931.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112931 |
| [19] | 孙佼佼, 郭英之. 古村落旅游地居民积极感知测度与多元影响路径--以昆山市周庄为例[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(6): 213-221. |
| [Sun Jiaojiao, Guo Yingzhi. Measurement of multiple influence paths of the residents’ positive perception in ancient village tourism destination:Taking Zhouzhuang, Kunshan City as an example[J]. Economic Geography, 2022, 42(6): 213-221.] | |
| [20] |
郭安禧, 郭英之, 梁丽芳, 等. 古镇旅游地居民旅游影响感知对支持旅游开发的影响--信任旅游开发公司的调节作用[J]. 世界地理研究, 2019, 28(6): 178-188.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.06.2018335 |
|
[Guo Anxi, Guo Yingzhi, Liang Lifang, et al. Influence of residents’ tourism impact perception on support for tourism development in ancient towns: Based on the moderating role of trusting in tourism development company[J]. World Regional Studies, 2019, 28(6): 178-188.]
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.06.2018335 |
|
| [21] | 吴丽敏, 黄震方, 谈志娟, 等. 江南文化古镇居民旅游影响感知及其形成机理--以同里为例[J]. 人文地理, 2015, 30(4): 143-148. |
| [Wu Limin, Huang Zhenfang, Tan Zhijuan, et al. Tourism impact perception of residents in Jiangnan ancient town and its formation mechanism: A case study of Tongli[J]. Human Geography, 2015, 30(4): 143-148.] | |
| [22] | 郭安禧, 郭英之, 李海军, 等. 旅游地社区居民旅游影响感知与生活质量感知关系研究[J]. 世界地理研究, 2017, 26(5): 115-127. |
| [Guo Anxi, Guo Yingzhi, Li Haijun, et al. Relationship between perceived tourism impacts and perceived quality of life of community residents in tourist destinations[J]. World Regional Studies, 2017, 26(5): 115-127.] | |
| [23] | 李观凤, 焦华富, 王群. 干旱区文化旅游地社会-生态系统恢复力年际变化及影响因素--以甘肃省敦煌市为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(3): 935-945. |
| [Li Guanfeng, Jiao Huafu, Wang Qun. Interannual variation and influencing factors of social-ecological system resilience of cultural tourism destination in arid area: A case of Dunhuang City, Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2022, 45(3): 935-945.] | |
| [24] |
刘博, 朱竑. 全球化形象与环保形象对消费行为意向的影响--基于国际快时尚品牌H&M的案例[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(4): 699-710.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201704011 |
|
[Liu Bo, Zhu Hong. Influence of perceived brand globalness and environmental image on consumption intentions: A case study of H&M[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(4): 699-710.]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201704011 |
|
| [25] | 娄伟. 观念认同与地区秩序建构--兼谈中国新安全观在建构东亚秩序中的作用[J]. 东南亚研究, 2012(1): 53-57. |
| [Lou Wei. Idea identity and regional order constructing: Also talking about the effects of China’s new concept of security on East Asia order[J]. Southeast Asian Studies, 2012(1): 53-57.] | |
| [26] |
马凌, 谢圆圆, 袁振杰. 新型全球化与流动性背景下知识移民研究: 议题与展望[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(7): 1129-1138.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.07.003 |
|
[Ma Ling, Xie Yuanyuan, Yuan Zhenjie. A review of intellectual migration research under the background of globalization and mobility: Topics and prospects[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2021, 41(7): 1129-1138.]
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.07.003 |
|
| [27] |
刘卫东. 新冠肺炎疫情对经济全球化的影响分析[J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39(7): 1439-1449.
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200514 |
|
[Liu Weidong. The impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the development of economic globalization[J]. Geographical Research, 2020, 39(7): 1439-1449.]
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200514 |
|
| [28] |
张捷, 卢韶婧, 杜国庆, 等. 中、日都市旅游街区书法景观空间分异及其文化认同比较研究[J]. 地理科学, 2014, 34(7): 831-839.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.07.831 |
|
[Zhang Jie, Lu Shaojing, Du Guoqing, et al. On spatial differentiation and related cultural identity of calligraphic landscapes in tourist districts: A comparative study between China and Japan[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(7): 831-839.]
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.07.831 |
|
| [29] |
张心怡, 张敏. 重大事故影响下的工人社区衰退机制与韧性--基于过滤理论的分析[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(2): 546-561.
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020210002 |
|
[Zhang Xinyi, Zhang Min. The decline and resilience of worker community under the influence of accidents: Based on filtering theory[J]. Geographical Research, 2022, 41(2): 546-561.]
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020210002 |
|
| [30] | 朱竑, 贾莲莲. 基于旅游“城市化”背景下的城市“旅游化”--桂林案例[J]. 经济地理, 2006, 26(1): 151-155. |
| [Zhu Hong, Jia Lianlian. The form of urban tourism based on the tourism urbanization[J]. Economic Geography, 2006, 26(1): 151-155.] | |
| [31] | 余国扬. 达沃斯现象研究[J]. 热带地理, 2003, 23(1): 13-17. |
| [Yu Guoyang. A study on Davos phenomenon[J]. Tropical Geography, 2003, 23(1): 13-17.] | |
| [32] | 周玲吉, 陈天. 瑞士洛桑城市规划经验对我国山水城市更新的启示[C]// 中国城市规划学会. 规划60年: 成就与挑战--2016中国城市规划年会论文集(14山地城乡规划). 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016: 311-318. |
| [Zhou Lingji, Chen Tian. Implications of the Lausanne urban planning experience for urban regeneration in China’s landscape[C]// Chinese Society of Urban Planning. 60 Years of Planning:Achievements and Challenges-Proceedings of the 2016 China Urban Planning Annual Conference (14 Mountain Urban and Rural Planning). Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2016: 311-318.] | |
| [33] | 王春雷, 涂天慧. 城市旅游目的地品牌资产管理研究--以荷兰阿姆斯特丹为例[J]. 全球城市研究, 2021, 2(2): 110-126, 193. |
| [Wang Chunlei, Tu Tianhui. Study on urban tourism destination brand equity management: Taking Amsterdam as an example[J]. Global Cities Research, 2021, 2(2): 110-126, 193.] | |
| [34] |
Joseph D R, Harry A C. Cultivating a global identity[J]. Journal of Social and Political Psychology, 2015, 3(2): 310-330.
doi: 10.5964/jspp.v3i2.507 |
| [35] | 余洋洋, 巫达. 全球化与在地化[J]. 广西民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2021, 43(4): 17-23. |
| [Yu Yangyang, Wu Da. Globalization and indigenization[J]. Journal of Guangxi Minzu University(Philosophy and Social Science Edition), 2021, 43(4): 17-23.] | |
| [36] | 封丹, 朱竑,Breitung W. 基于居民感知的跨界意义研究--以深港跨界居民为例[J]. 人文地理, 2019, 34(3): 53-60. |
| [Feng Dan, Zhu Hong, Breitung W. The interactions between cross-border mobility, sense of place and border perceptions: A case of Hong Kong and Shenzhen border crossers[J]. Human Geography, 2019, 34(3): 53-60.] | |
| [37] |
Zhu H, Qian J X, Gao Y. Globalization and the production of city image in Guangzhou’s metro station advertisements[J]. Cities, 2011, 28(3): 221-229.
doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2010.12.004 |
| [38] |
文彤, 张玉林, 梁祎. 公众视角下的地方与无地方: 基于游客饮食体验感知的研究[J]. 热带地理, 2020, 40(5): 775-785.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003277 |
|
[Wen Tong, Zhang Yulin, Liang Yi. Place and placelessness: The perception of tourists’ local food taste in Hong Kong[J]. Tropical Geography, 2020, 40(5): 775-785.]
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003277 |
|
| [39] |
吴偲, 朱竑, 李军. 粤港澳大学生的美展感知及地方感影响差异: 基于多群组结构方程模型分析[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(4): 645-655.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.04.011 |
|
[Wu Cai, Zhu Hong, Li Jun. Differences in the impact of art exhibition perception and sense of place among college students from Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macau: Model analysis based on multi-group structural equation[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 645-655.]
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.04.011 |
|
| [40] |
卢松, 李卓妍. 城市居民对大型活动影响的感知与态度模式--以首届中国国际进口博览会为例[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(12): 3025-3042.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202112011 |
|
[Lu Song, Li Zhuoyan. Urban residents’ perceptions and attitudes towards the impacts of mega-event: A case study of the first China International Import Expo[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(12): 3025-3042.]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202112011 |
|
| [41] | 袁玲燕, 张玥. 旅游与全球化关系研究进展及启示[J]. 世界地理研究, 2018, 27(6): 115-126. |
| [Yuan Lingyan, Zhang Yue. The research progress and enlightenments of the relationship between tourism and globalization[J]. World Regional Studies, 2018, 27(6): 115-126.] | |
| [42] | 徐茗, 卢松. 城市语言景观研究进展及展望[J]. 人文地理, 2015(1): 21-25. |
| [Xu Ming, Lu Song. Research progress and prospect of urban linguistic landscape[J]. Human Geography, 2015(1): 21-25.] | |
| [43] |
敖荣军, 常亮. 基于结构方程模型的中国县域人口老龄化影响机制[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(8): 1572-1584.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202008002 |
|
[Ao Rongjun, Chang Liang. Influencing mechanism of regional ageing in China based on the structural equation model[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020, 75(8): 1572-1584.]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202008002 |
| [1] | 郭燕, 张志斌, 陈龙, 马晓敏, 赵学伟. 居住自选择视角下城市建成环境对通勤模式选择的影响——以兰州市主城区为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2024, 47(2): 307-318. |
| [2] | 吴海娟, 郑芳, 易洁琰. 生态移民村镇居民居住满意度及其影响因素研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(8): 1387-1396. |
| [3] | 姚岚博, 冶建明, 王芸, 朱现伟. 干旱区人居环境系统耦合协调的时空演变及作用机制研究——以新疆为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(6): 1013-1023. |
| [4] | 韩大勇, 牛忠泽, 伍永明, 高健. 水热条件共同驱动新疆湿地植物丰富度空间分布格局[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(1): 86-93. |
| [5] | 李观凤,焦华富,王群. 干旱区文化旅游地社会-生态系统恢复力年际变化及影响因素——以甘肃省敦煌市为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(3): 935-945. |
| [6] | 杨人豪, 杨庆媛, 印文, 李元庆. 基于结构方程模型的休耕地管护意愿及行为分析——以河北省邢台市为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(1): 260-270. |
| [7] | 周俊俊, 杨美玲, 樊新刚, 肖成权, 贾红丽. 基于结构方程模型的农户生态补偿参与意愿影响因素研究——以宁夏盐池县为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(5): 1185-1194. |
| [8] | 骆丽, 吴云清. 基于结构方程模型的城市邻避设施风险可接受度研究—以天长市为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(2): 452-457. |
| [9] | 王岩,杨俊孝. 西部地区农村劳动力转移对农用地流转意愿的影响——以新疆玛纳斯为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2015, 38(2): 411-419. |
| [10] | 由亚男,卢小静,张志敏. 旅游目的地传统风俗影响因素与模型构建——以喀什地区为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2012, 35(5): 822-828. |
|
||
