干旱区地理 ›› 2023, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 1663-1679.doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.596 cstr: 32274.14.ALG2022596
马运强1,2( ),刘瑞1,2,李志忠1,2,3(
),刘瑞1,2,李志忠1,2,3( ),靳建辉1,2,3,邹晓君1,2,谭典佳1,2,陶通炼1,2
),靳建辉1,2,3,邹晓君1,2,谭典佳1,2,陶通炼1,2
收稿日期:2022-11-12
修回日期:2022-12-07
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-11-10
作者简介:马运强(1998-),男,硕士研究生,主要从事风沙地貌与环境演变研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
MA Yunqiang1,2( ),LIU Rui1,2,LI Zhizhong1,2,3(
),LIU Rui1,2,LI Zhizhong1,2,3( ),JIN Jianhui1,2,3,ZOU Xiaojun1,2,TAN Dianjia1,2,TAO Tonglian1,2
),JIN Jianhui1,2,3,ZOU Xiaojun1,2,TAN Dianjia1,2,TAO Tonglian1,2
Received:2022-11-12
Revised:2022-12-07
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-11-10
摘要:
古尔班通古特沙漠南缘处在风、水两相营力作用的交汇区域,沉积环境独特,对气候变化响应敏感,是研究中国西北沙区全新世环境演变的理想区域。选取古尔班通古特沙漠南缘荒漠-绿洲过渡带3个风积-冲积交互地层剖面,在实地观察岩性特征、沉积序列的基础上,通过光释光(OSL)测年建立年代标尺,结合粒度参数、磁化率和石英颗粒表面微形态特征的对比分析,综合判别研究区全新世以来的沉积环境演化过程。结果表明:研究区地层序列主要反映了河流过程和风沙过程的消长,并且表现出同期异相特征。约11.8~10.2 ka,天山北麓冲积作用活跃,辫状河深入沙漠,局部发育河流沉积;约10.2~6.0 ka,研究区进入全新世适宜期,沙漠北退,河湖、湿地广泛发育;约6 ka至今,研究区冲积作用减弱,风沙活动频繁,沙漠环境与河流环境交替出现。近千年以来,研究区沉积环境表现出风沙活动增强、河流冲积萎缩的特点,古尔班通古特沙漠总体上有南侵扩张趋势。本区全新世湿润环境的出现主要受制于西风环流的强弱变化和位置变动,此外,北半球夏季太阳辐射与天山冰川的耦合作用及北大西洋冷事件引发的气候波动可能也是影响本区全新世沉积环境变迁的重要因素。
马运强, 刘瑞, 李志忠, 靳建辉, 邹晓君, 谭典佳, 陶通炼. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘沉积记录的全新世环境演变[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(10): 1663-1679.
MA Yunqiang, LIU Rui, LI Zhizhong, JIN Jianhui, ZOU Xiaojun, TAN Dianjia, TAO Tonglian. Holocene environmental evolution recorded by sedimentation on the southern edge of the Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(10): 1663-1679.
表1
研究区剖面OSL测年样品的年代及相关参数值"
| 样号 | 埋深/m | 铀(U)/μg·g-1 | 钍(Th)/μg·g-1 | 钾(K)/μg·g-1 | 含水率/% | 环境剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量/Gy | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XMOSL1 | 2.75 | 1.44±0.05 | 5.47±0.05 | 2.08±0.01 | 5±1 | 2.78±0.04 | 12.95±4.17 | 4.66±1.50 |
| XMOSL2 | 3.00 | 1.37±0.05 | 4.74±0.05 | 2.06±0.01 | 5±1 | 2.71±0.04 | 13.04±3.19 | 4.82±1.18 |
| XMOSL3 | 3.50 | 1.43±0.05 | 4.98±0.05 | 2.09±0.01 | 5±1 | 2.77±0.04 | 13.81±1.30 | 4.99±0.47 |
| MGOSL1 | 0.55 | 3.57±0.04 | 12.3±0.15 | 2.45±0.02 | 5±5 | 5.04±0.37 | 8.74±0.40 | 1.73±0.15 |
| MGOSL2 | 1.55 | 2.54±0.05 | 9.52±0.09 | 2.07±0.02 | 5±5 | 3.34±0.14 | 8.15±0.18 | 2.44±0.12 |
| MGOSL3 | 2.50 | 2.27±0.04 | 7.78±0.15 | 2.06±0.02 | 5±5 | 3.72±0.28 | 9.06±0.39 | 2.43±0.21 |
| MGOSL4 | 2.75 | 2.57±0.04 | 8.50±0.16 | 2.05±0.02 | 5±5 | 3.88±0.29 | 9.33±0.20 | 2.41±0.19 |
| MGOSL5 | 3.10 | 3.52±0.10 | 11.6±0.30 | 2.24±0.01 | 5±5 | 4.69±0.35 | 10.53±0.85 | 2.25±0.25 |
| XQOSL1 | 0.66 | 1.51±0.01 | 7.78±0.10 | 1.91±0.02 | 5±5 | 2.87±0.12 | 11.48±0.76 | 4.01±0.31 |
| XQOSL2 | 1.26 | 1.24±0.01 | 5.25±0.09 | 2.01±0.01 | 5±5 | 2.72±0.11 | 15.65±1.06 | 5.76±0.46 |
| XQOSL3 | 3.25 | 1.02±0.01 | 3.51±0.02 | 1.63±0.02 | 5±5 | 2.14±0.09 | 23.08±0.80 | 10.79±0.59 |
| XQOSL4 | 4.05 | 0.94±0.01 | 3.02±0.03 | 1.75±0.01 | 5±5 | 2.19±0.09 | 24.32±1.27 | 11.11±0.75 |
表2
研究剖面沉积类型及其特征"
| 类型 | 沉积构造 | 粒度 | 磁化率 | 石英砂形态及表面结构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沙丘沉积 | 交错层理 | 以细沙、极细沙为主;负偏尖峰;分选良好 | 较高 | 近圆状;麻坑、碟形坑、溶蚀坑及硅沉淀 |
| 沙席沉积 | 水平层理 | 以极细沙为主,细沙次之;正态尖峰;分选良好 | 较高 | 近圆状;麻坑、碟形坑;硅沉淀及裂纹 |
| 静水沉积 | 块状构造,不显层理 | 黏土、粉沙含量高;正偏宽峰;分选差 | 低 | 棱角状;流水磨光面;三角坑;硅质鳞片及硅质球 |
| 漫洪沉积 | 块状构造 | 粉沙含量高,黏土次之;峰态宽平;分选较差 | 低 | 次棱角状;V形坑、挤压坑;贝壳状断口;硅沉淀 |
| 河漫滩沉积 | 波状层理,夹黏土球、黏土碎块 | 以粉沙为主;负偏宽峰;分选较差 | 较低 | - |
| 漫滩湿地沉积 | 根孔锈斑,水下沙波纹 | 以粉沙为主;正态宽峰;分选中等 | 低 | - |
| 河床沉积 | 槽状交错层理 | 中沙含量高,细沙次之;正偏尖峰;分选较好 | 高 | 次圆状;V形坑、圆形坑;贝壳状断口 |
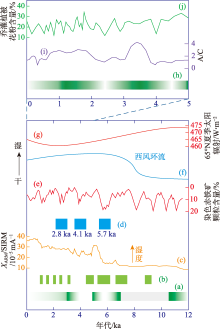
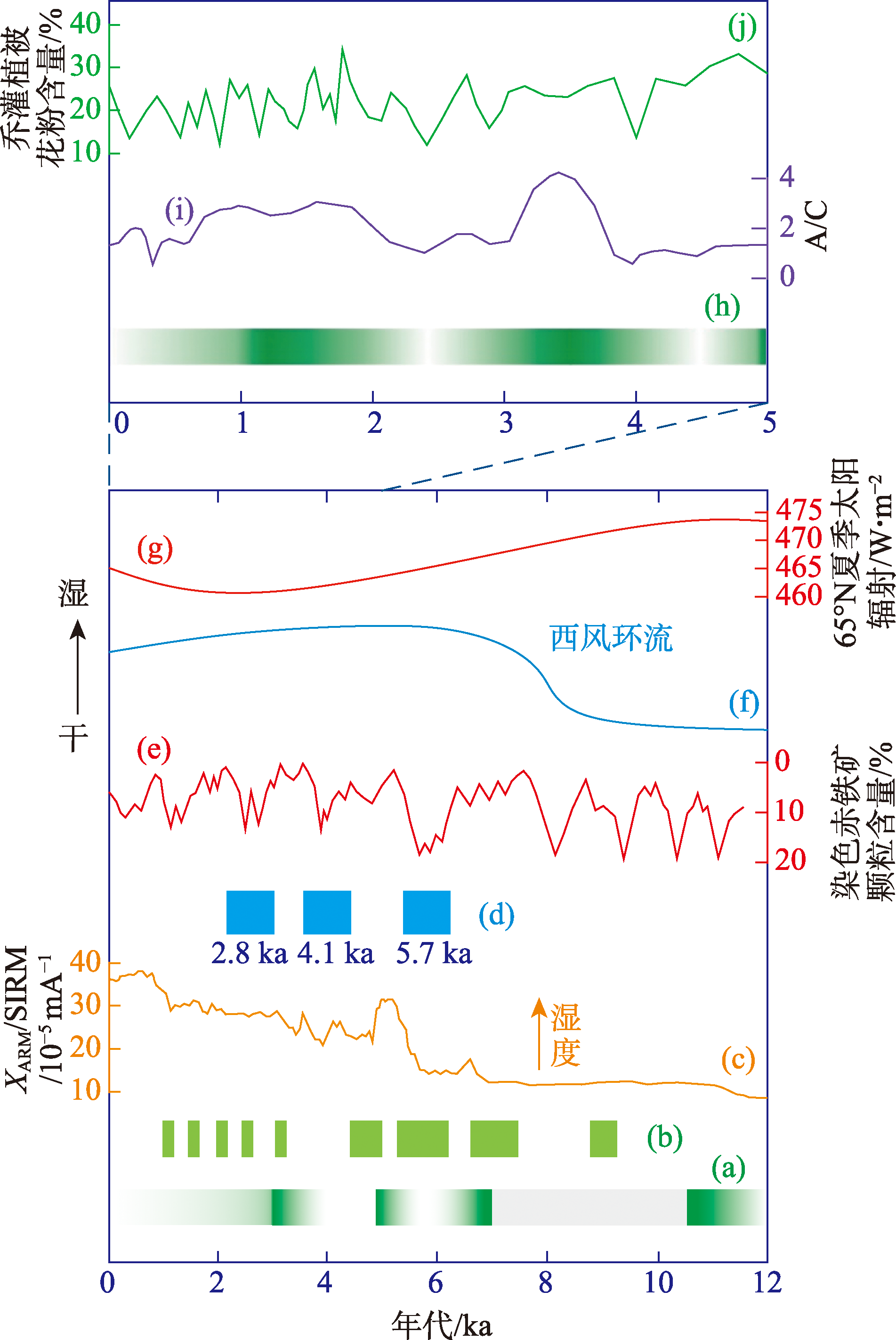
图9
本研究揭示的古尔班通古特沙漠南缘全新世环境演变过程与周边区域地质记录的对比 注:(a) XQ剖面沉积序列记录的全新世沙漠南缘的湿度变化过程,绿色部分代表湿润期,渐变色部分代表湿度增加或减弱期,灰色部分代表缺少年代控制而导致的湿度记录缺失;(b) 莫索湾沙垄剖面古土壤序列(改绘自文献[17]);(c) 天山北麓LJW10剖面XARM/SIRM[21];(d) 北天山冰进期[81];(e) 北大西洋染色赤铁矿颗粒含量[88];(f) 西风环流强度变化[20];(g) 65°N夏季太阳辐射强度变化[76-77];(h) MG、XM剖面沉积序列记录的5 ka以来沙漠南缘的湿度变化过程;(i) 阿尔泰山南部NRX泥炭蒿黎比(A/C)[86];(j) 喀纳斯湖乔木、灌木花粉含量[87]。"
| [1] | Goudie A S. Great warm deserts of the world: Landscapes and evolution[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2002: 14-15. |
| [2] | Parsons A J, Abrahams A D. Geomorphology of desert environments[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 135-141. |
| [3] |
Yang X P, Li H W, Conacher A. Large-scale controls on the development of sand seas in northern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 250: 74-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.03.052 |
| [4] | Warren A. Dunes: Dynamics, morphology, history[M]. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013: 45-47. |
| [5] | Williams M. Climate change in deserts: Past, present and future[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 2014: 25-34. |
| [6] | Thomas D S G, Hesse P. Dune paleoenvironments[C]//Treatise on Geomorphology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2022: 592-616. |
| [7] | Goudie A S, Middleton N J. Desert dust in the global system[M]. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006: 45-47. |
| [8] |
Bristow C S, Armitagea S J. Dune ages in the sand deserts of the southern Sahara and Sahel[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 410(29): 46-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.07.062 |
| [9] |
Thomas D S G, Bailey R M. Is there evidence for global-scale forcing of southern Hemisphere Quaternary desert dune accumulation? A quantitative method for testing hypotheses of dune system development[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2017, 42(14): 2280-2294.
doi: 10.1002/esp.v42.14 |
| [10] |
Lu H Y, Yi S W, Xu Z W, et al. Chinese deserts and sand fields in Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene optimum[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(23): 2775-2783.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5919-7 |
| [11] |
Li Q, Wu H B, Guo Z T, et al. Distribution and vegetation reconstruction of the deserts of northern China during the mid-Holocene[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(14): 5184-5191.
doi: 10.1002/grl.v41.14 |
| [12] | 董光荣, 陈惠中, 王贵勇, 等.150 ka以来中国北方沙漠沙地演化和气候变化[J]. 中国科学(B辑: 化学, 生命科学, 地学), 1995(12): 1303-1312. |
| [Dong Guangrong, Chen Huizhong, Wang Guiyong, et al. Desert and sandy land evolution and climate change in northern China since 150 ka[J]. Science China Press (Series B: Chemical, Biology, Geography), 1995(12): 1303-1312. ] | |
| [13] | 吴正. 中国沙漠及其治理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 10-11. |
| [Wu Zheng. Chinese desert and its governance[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 10-11. ] | |
| [14] |
Yang X P, Scuderi L, Paillou P, et al. Quaternary environmental changes in the drylands of China: A critical review[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(23-24): 3219-3233.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.08.009 |
| [15] |
Bush A B G, Rokosh D, Rutter N W, et al. Desert margins near the Chinese Loess Plateau during the mid-Holocene and at the Last Glacial Maximum: A model-data intercomparison[J]. Glob Planet Change, 2002, 32: 361-374.
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00076-0 |
| [16] |
Yang X P, Liang P, Zhang D G, et al. Holocene aeolian stratigraphic sequences in the eastern portion of the desert belt (sand seas and sandy lands) in northern China and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2019, 62(8): 1302-1315.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9304-y |
| [17] | 陈惠中, 金炯, 董光荣. 全新世古尔班通古特沙漠演化和气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2001, 21(4): 18-24. |
| [Chen Huizhong, Jin Jiong, Dong Guangrong. Holocene evolution processes of Gurbantunggut Desert and climatic changes[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2001, 21(4): 18-24. ] | |
| [18] |
Li S H, Fan A C. OSL chronology of sand deposits and climate change of last 18 ka in Gurbantunggut Desert, northwest China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2011, 26(8): 813-818.
doi: 10.1002/jqs.v26.8 |
| [19] | Jin L Y, Chen F H, Morrill C, et al. Causes of early Holocene desertification in arid Central Asia[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2012, 8: 1577-1591. |
| [20] |
Chen F H, Yu Z C, Yang M L, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid Central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3-4): 351-364.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.10.017 |
| [21] |
Chen F H, Jia J, Chen J H, et al. A persistent Holocene wetting trend in arid Central Asia, with wettest conditions in the late Holocene, revealed by multi-proxy analyses of loess-paleosol sequences in Xinjiang, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 146(2): 134-146.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.002 |
| [22] |
Rao Z G, Wu D D, Shi F X, et al. Reconciling the “westerlies” and “monsoon” models: A new hypothesis for the Holocene moisture evolution of the Xinjiang region, NW China[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2019, 191(1): 263-272.
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.002 |
| [23] | 黄强, 周兴佳. 晚更新世晚期以来古尔班通古特沙漠南部的气候环境演化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2000, 23(1): 55-60. |
| [Huang Qiang, Zhou Xingjia. The climate-environment changes in the south of Gurbantunggut Desert since 80 ka BP[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2000, 23(1): 55-60. ] | |
| [24] | Zong H R, Fu X, Li Z J, et al. Multi-method pIRIR dating of sedimentary sequences at the southern edge of the Gurbantunggut Desert, NW China and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2022, 70: 101300, doi: 10.1016/j.quageo. 2022.101300. |
| [25] | 阎顺, 穆桂金, 孔昭宸, 等. 天山北麓晚全新世环境演变及其人类活动的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2004, 26(4): 403-410. |
| [Yan Shun, Mu Guijin, Kong Zhaochen, et al. Environmental evolvement and human activity impact in the late Holocene on the north slopes of the Tianshan Mountains, China[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2004, 26(4): 403-410. ] | |
| [26] | 阎顺, 李树峰, 孔昭宸, 等. 乌鲁木齐东道海子剖面的孢粉分析及其反映的环境变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(4): 463-468. |
| [Yan Shun, Li Shufeng, Kong Zhaochen, et al. The pollen analyses and environment changes of the Dongdaohaizi area in Urumqi, Xinjiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(4): 463-468. ] | |
| [27] | 李树峰, 阎顺, 孔昭宸, 等. 乌鲁木齐东道海子剖面的硅藻记录与环境演变[J]. 干旱区地理, 2005, 28(1): 81-87. |
| [Li Shufeng, Yan Shun, Kong Zhaochen, et al. Diatom records and environmental changes of the Dongdaohaizi area in Urumqi, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2005, 28(1): 81-87. ] | |
| [28] | 马妮娜, 穆桂金, 阎顺. 中全新世以来乌鲁木齐东道海子B剖面沉积物源探讨与分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2005, 28(2): 188-193. |
| [Ma Nina, Mu Guijin, Yan Shun. Discussion and analysis on sediment source of Dongdaohaizi B section in Urumqi since middle Holocene[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2005, 28(2): 188-193. ] | |
| [29] | 陈治平. 准噶尔盆地古尔班通古特沙漠的基本特征[C]// 地理集刊(地貌学). 北京: 科学出版社, 1963(5): 79-91. |
| [Chen Zhiping. Basic features of Gurbantunggut Desert in Junggar Basin[C]// Geographical Collection (Geomorphology). Beijing: Science Press, 1963(5): 79-91. ] | |
| [30] | 朱震达, 吴正, 刘恕. 中国沙漠概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980: 1-107. |
| [Zhu Zhenda, Wu Zheng, Liu Shu. Generality to Chinese desert[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980: 1-107. ] | |
| [31] | 陈曦. 中国干旱区自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 45-46. |
| [Chen Xi. Natural geography of arid areas in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 45-46. ] | |
| [32] | 钱亦兵, 吴兆宁. 古尔班通古特沙漠环境研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 6-15. |
| [Qian Yibing, Wu Zhaoning. Environments of Gurbantunggut Desert[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 6-15. ] | |
| [33] | 中国科学院新疆综合考察队. 新疆地貌[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 56-58. |
| [Xinjiang Expedition of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Xinjiang landform[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1978: 56-58. ] | |
| [34] | Li X M, Yan P, Liu B L. Geomorphological classification of aeolian-fluvial interactions in the desert region of north China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2020, 172: 104021, doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2019.104021. |
| [35] | Aitken M J. An introduction to optical dating[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998: 1-262. |
| [36] | Stokes S, Bailey R M, Fedoroff N, et al. Optical dating of aeolian dynamism on the west African Sahelian margin[M]. Geomorphology, 2004, 59(1-4): 281-291. |
| [37] | Robins L, Greenbaum N, Yu L P, et al. High resolution portable OSL analysis of vegetated linear dune construction in the margins of the northwestern Negev dunefield (Israel) during the late Quaternary[J]. Aeolian Research, 2021, 50: 100680, doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2021.100680. |
| [38] |
赖忠平, 欧先交. 光释光测年基本流程[J]. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(5): 683-693.
doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.05.001 |
|
[Lai Zhongping, Ou Xianjiao. Basic process of optically stimulated luminescence dating[J]. Progress of Geography, 2013, 32(5): 683-693. ]
doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.05.001 |
|
| [39] |
Murray A S, Wintle A G. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(1): 57-73.
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X |
| [40] | 王旭龙, 卢演俦, 李晓妮. 细颗粒石英光释光测年:简单多片再生法[J]. 地震地质, 2005, 27(4): 615-622. |
| [Wang Xulong, Lu Yanchou, Li Xiaoni. Luminescence dating of fine-grained quartz in Chinese loess-simplified multiple aliquot regenerative-dose (MAR) protocol[J]. Seismology Geology, 2005, 27(4): 615-622. ] | |
| [41] |
Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos river bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1): 3-26.
doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D |
| [42] | Reading H G. Sedimentary environments and facies[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 1978: 1-557. |
| [43] | 任明达, 王乃梁. 现代沉积环境概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981: 77-94. |
| [Ren Mingda, Wang Nailiang. Generality to modern sedimentary environments[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981: 77-94. ] | |
| [44] | 杨小平, 杜金花, 梁鹏, 等. 晚更新世以来塔克拉玛干沙漠中部地区的环境演变[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(24): 3205-3218. |
| [Yang Xiaoping, Du Jinhua, Liang Peng, et al. Paleoenvironmental changes in the central part of the Taklamakan Desert, northwestern China since the late Pleistocene[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(24): 3205-3218. ] | |
| [45] | 成都地质学院陕北队. 沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 1-147. |
| [Team Northern Shaanxi of Chengdu Institute of Geology. Grain size analysis of sedimentary rocks and its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1978: 1-147. ] | |
| [46] | Scholle P A, Spearing S. Sandstone depositional environments[M]. Tulsa: The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1981: 49-83. |
| [47] |
Lee D B, Ferdowsi B, Jerolmack D J. The imprint of vegetation on desert dune dynamics[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(21): 12041-12048.
doi: 10.1029/2019GL084177 |
| [48] | Thompson R, Oldfield F. Environmental magnetism[M]. London: Allen & Unwin, 1986: 56-57. |
| [49] |
Heller F, Liu T S. Paleoclimatic and sedimentary history from magnetic susceptibility of loess in China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1986, 13: 1169-1172.
doi: 10.1029/GL013i011p01169 |
| [50] | 吕厚远, 韩家懋, 吴乃琴, 等. 中国现代土壤磁化率分析及其古气候意义[J]. 中国科学(B辑: 化学, 生命科学, 地学), 1994, 24(12): 1291-1297. |
| [Lü Houyuan, Han Jiamao, Wu Naiqin, et al. Analysis of modern soil magnetic susceptibility of loess in China paleoclimate significance[J]. Science China (Series B: Chemical, Biology, Geography), 1994, 24(12): 1291-1297. ] | |
| [51] | 刘秀铭, 刘植, 吕镔, 等. 塞尔维亚黄土的磁学性质及其环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(33): 3173-3184. |
| [Liu Xiuming, Liu Zhi, Lü Bin, et al. The magnetic properties of Serbian loess and its environmental significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(33): 3173-3184. ] | |
| [52] | 李平原, 刘秀铭, 刘植, 等. 腾格里沙漠边缘表土磁学性质及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 3(4): 771-776. |
| [Li Pingyuan, Liu Xiuming, Liu Zhi, et al. The magnetic properties of topsoil from the edge of Tenger Desert, and its environmental significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(4): 771-776. ] | |
| [53] | 李平原, 刘秀铭, 郭雪莲, 等. 西北戈壁沙漠-黄土高原区表土磁化率特征及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(2): 360-367. |
| [Li Pingyuan, Liu Xiuming, Guo Xuelian, et al. The magnetic susceptibility properties of top soil’s in Gobi-Loess Plateau, northwest China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(2): 360-367. ] | |
| [54] | 张家强, 李从先, 丛友滋. 水成沉积与风成沉积及古土壤的磁组构特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2): 86-95. |
| [Zhang Jiaqiang, Li Congxian, Cong Youzi. Magnetic fabric characteristics of hydraulic deposit, eolian deposit and paleosol[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 86-95. ] | |
| [55] | 夏敦胜, 魏海涛, 马剑英, 等. 中亚地区现代表土磁学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(6): 937-946. |
| [Xia Dunsheng, Wei Haitao, Ma Jianying, et al. Magnetic characteristics of surface soil in arid region of Central Asia and their paleoenvironment significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(6): 937-946. ] | |
| [56] |
赵爽, 夏敦胜, 靳鹤龄, 等. 科尔沁沙地风沙沉积物磁学特征及其古环境意义初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 334-342.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00047 |
|
[Zhao Shuang, Xia Dunsheng, Jin Heling, et al. Magnetic characteristics of aeolian sand sediments in Horqin Sandy Land, northeastern China, and its paleoenvironment significance: A preliminary exploration[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2013, 33(2): 334-342. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00047 |
|
| [57] | 吉云平. 不同类型沉积物中磁化率的解释[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2007. |
| [Ji Yunping. Interpretation of magnetic susceptibility in different sediments[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2007. ] | |
| [58] |
Xia D S, Jia J, Wei H T, et al. Magnetic properties of surface soils in the Chinese Loess Plateau and the adjacent Gobi areas, and their implication for climatic studies[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2012, 78: 73-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.10.012 |
| [59] |
王友郡, 贾佳, 高福元, 等. 阿拉善地区古水下沉积物与风沙沉积物磁学特征及意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(4): 626-634.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2016.00026 |
|
[Wang Youjun, Jia Jia, Gao Fuyuan, et al. Magnetic characteristics of aeolian sand and ancient underwater sediments and their applications in Alxa region of China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2017, 37(4): 626-634. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2016.00026 |
|
| [60] | 吉云平, 夏正楷. 不同类型沉积物磁化率的比较研究和初步解释[J]. 地球学报, 2007, 28(6): 541-549. |
| [Ji Yunping, Xia Zhengkai. Comparison and primarily interpretation of magnetic susceptibility in different sediment[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2007, 28(6): 541-549. ] | |
| [61] |
Maher B A, Thompson R. Paleorainfall reconstructions from pedogenic magnetic susceptibility variations in Chinese loess and paleosols[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(3): 383-391.
doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1083 |
| [62] | 刘秀铭, 夏敦胜, 刘东生, 等. 中国黄土和阿拉斯加黄土磁化率气候记录的两种模式探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(2): 210-220. |
| [Liu Xiuming, Xia Dunsheng, Liu Dongsheng, et al. Discussion on two models of paleoclimatic records of magnetic susceptibility of Alaskan and Chinese loess[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(2): 210-220. ] | |
| [63] | 刘秀铭, 刘东生, 夏敦胜, 等. 中国与西伯利亚黄土磁化率古气候记录-氧化和还原条件下的两种成土模式分析[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2007, 37(10): 1382-1391. |
| [Liu Xiuming, Liu Dongsheng, Xia Dunsheng, et al. The analyses of two different pedogenesis models in reductive and oxidative conditions recorded by Chinese and Siberia loess[J]. Science China Press (Series D:Geoscience), 2007, 37(10): 1382-1391. ] | |
| [64] | 谢又予, 崔之久, 李洪云. 中国石英砂表面结构特征图谱[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984: 1-164. |
| [Xie Youyu, Cui Zhijiu, Li Hongyun. Atlas of surface structure characteristics of Chinese quartz sand[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984: 1-164. ] | |
| [65] | 吴正. 我国内陆沙漠与海岸沙丘石英颗粒表面结构的对比研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 1995, 5(3): 201-206. |
| [Wu Zheng. A comparative study of the surface texture of quartz sand in inland deserts and than in coastal dunes, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1995, 5(3): 201-206. ] | |
| [66] | 高存海, 穆桂金, 阎顺, 等. 塔克拉玛干沙漠深部石英砂微结构特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质论评, 1995, 41(2): 152-158. |
| [Gao Cunhai, Mu Guijin, Yan Shun, et al. Features of surface micro-textures of quartz sand grains in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert and their environmental significance[J]. Geological Review, 1995, 41(2): 152-158. ] | |
| [67] |
朱春鸣, 董治宝, 刘铮瑶, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠树枝状沙丘沉积物粒度和微形态特征的空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 9-18.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00118 |
|
[Zhu Chunming, Dong Zhibao, Liu Zhengyao, et al. Grain size and micro-morphology characteristics of the surface sediments of dendritic sand dunes in the Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 9-18. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00118 |
|
| [68] | 刘铮瑶. 古尔班通古特沙漠沙丘地貌及其发育环境[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2022. |
| [Liu Zhengyao. Sandy landform and development environment of Gurbantunggut Desert[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2022. ] | |
| [69] | 吴敬禄, 沈吉, 王苏民, 等. 新疆艾比湖地区湖泊沉积记录的早全新世气候环境特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2003, 33(6): 569-575. |
| [Wu Jinglu, Shen Ji, Wang Sumin, et al. Characteristics of early Holocene climate and environment recorded by lake sediments in Ebinur Lake area, Xinjiang[J]. Science China Press (Series D: Geoscience), 2003, 33(6): 569-575. ] | |
| [70] | 宋姝瑶. 新疆艾比湖湿地全新世以来环境演变研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2016. |
| [Song Shuyao. Holocene climate change in the Ebinur Lake Wetland, Xinjiang, China[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University, 2016. ] | |
| [71] |
Li G H, Xia D S, Lu H, et al. Magnetic, granulometric and geochemical characterizations of loess sections in the eastern arid Central Asia: Implication for paleoenvironmental interpretations[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 552: 135-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.01.003 |
| [72] | 范义姣, 田伟东, 杨军怀, 等. 新疆天山地区不同海拔黄土记录的末次冰消期以来的环境演变[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(5): 1244-1253. |
| [Fan Yijiao, Tian Weidong, Yang Junhuai, et al. Environmental changes since last deglaciation recorded in loess at different altitude in Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(5): 1244-1253. ] | |
| [73] | Gao F Y, Jia J, Xia D S, et al. Assessment of the dominant climatic factor affecting pedogenic development in eolian sequences during the Holocene in arid Central Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 502(A): 78-84. |
| [74] | Kang S G, Wang X L, Roberts H M, et al. Increasing effective moisture during the Holocene in the semiarid regions of the Yili Basin, Central Asia: Evidence from loess sections[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 246: 106553, doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106553. |
| [75] | Jia J, Chen J H, Wang Z Y, et al. No evidence for an anti-phased Holocene moisture regime in mountains and basins in Central Asian: Records from Ili loess, Xinjiang[J]. Paleogeography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, 2021, 572: 110407, doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110407. |
| [76] |
Berger A, Loutre M F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million year[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(4): 297-317.
doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q |
| [77] |
Robutel P, Joutel F, Correia A C M, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the earth[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261-285.
doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041335 |
| [78] | 林瑞芬, 卫克勤, 程致远, 等. 新疆玛纳斯湖沉积柱样的古气候古环境研究[J]. 地球化学, 1996, 25(1): 63-72. |
| [Lin Ruifen, Wei Keqin, Cheng Zhiyuan, et al. A paleoclimatic study on lacustrine cores from Lake Manas, Xinjiang, western China[J]. Geochemical, 1996, 25(1): 63-72. ] | |
| [79] | 吴敬禄, 王苏民, 王洪道. 新疆艾比湖全新世以来的环境变迁与古气候[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1996, 27(5): 524-530. |
| [Wu Jinglu, Wang Sumin, Wang Hongdao. Characters of the evolution of climate and environment of Holocene in Aibi Lake Basin in Xinjiang[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia sinica, 1996, 27(5): 524-530. ] | |
| [80] | 史兴民, 李有利, 杨景春. 新疆玛纳斯河蘑菇湖沉积物中粘土矿物及其环境意义[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007, 30(1): 84-88. |
| [Shi Xingmin, Li Youli, Yang Jingchun. Environmental significance and clay mineral characteristics of Mogu Lake sediment of Manas River[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2007, 30(1): 84-88. ] | |
| [81] | 陈吉阳. 天山乌鲁木齐河源全新世冰川变化的地衣年代学等若干问题之初步研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑: 化学, 生物学, 农学, 医学,地学), 1988(1): 95-104. |
| [Chen Jiyang. A preliminary study on lichen chronology of Holocene glacier changes in the headwaters of Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains[J]. Science China (Series B: Chemical, Biology, Agronomy, Medical, Geography), 1988(1): 95-104. ] | |
| [82] | 汪海燕, 岳乐平, 李建星, 等. 全新世以来巴里坤湖面积变化及气候环境记录[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1): 93-100. |
| [Wang Haiyan, Yue Leping, Li Jianxing, et al. Changing of the lake area and records of climate and environment of Barkol Lake during Holocene[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 93-100. ] | |
| [83] |
Xie H C, Zhang H W, Ma J Y, et al. Trend of increasing Holocene summer precipitation in arid Central Asia: Evidence from an organic carbon isotopic record from the LJW10 loess section in Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Paleogeography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, 2018, 509: 24-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.04.006 |
| [84] |
延琪瑶, 王力, 张芸, 等. 新疆艾比湖小叶桦湿地3900年以来的植被及环境演变[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(2): 486-494.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202102.007 |
|
[Yan Qiyao, Wang Li, Zhang Yun, et al. Changes in vegetation and environment in the Betula microphylla wetland of Ebinur Lake in Xinjiang since 3900 cal aBP[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(2): 486-494. ]
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202102.007 |
|
| [85] |
Feng Z D, Sun A Z, Abdusalih N, et al. Vegetation changes and associated climatic changes in the southern Altai Mountains within China during the Holocene[J]. The Holocene, 2017, 27(5): 683-693.
doi: 10.1177/0959683616670469 |
| [86] | Zhang D L, Chen X, Li Y M, et al. Holocene moisture variations in the arid Central Asia: New evidence from the southern Altai Mountains of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 735: 139545, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139545. |
| [87] |
Haung X Z, Peng W, Rudaya N, et al. Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics in the Altai Mountains and surrounding areas[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(13): 6628-6636.
doi: 10.1029/2018GL078028 |
| [88] |
Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M, et al. A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in north Atlantic Holocene and glacial climates[J]. Science, 1997, 278(5341): 1257-1266.
doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1257 |
| [1] | 杨锐, 李建勇, 王宁练, 陈小俊, 杜建峰, 刘剑波, 韩岳婷. 西天山温泉地区全新世沉积物元素地球化学记录及其古环境意义[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(6): 900-910. |
| [2] | 徐宇杰, 刘冰, 孙爱军, 汪克奇, 李冬雪, 赵晖. 古尔班通古特沙漠及周边区域全新世环境演变研究进展[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(4): 550-562. |
| [3] | 刘瑞,李志忠,靳建辉,解锡豪,邹晓君,马运强. 古尔班通古特沙漠西南缘新月形沙丘内部沉积构造特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(3): 802-813. |
| [4] | 张峰,夏倩倩,迪丽拜尔·吐尔孙,刘建宗. 克里雅河尾闾圆沙三角洲古河道剖面所记录全新世古绿洲环境变化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(1): 178-187. |
| [5] | 李晓刚, 黄春长, 庞奖励. 无定河下游全新世古洪水研究 [J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(2): 380-387. |
| [6] | 王泽锋, 胡顺军, 李浩. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘丘间地梭梭群落蒸散特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(6): 1303-1309. |
| [7] | 段炎武, 孙青, 谢曼曼, 侯居峙, 梁洁, 李国强, 陈发虎. 新疆天山黄土GDGTs重建的全新世温度逐步升高及其可能意义[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(3): 528-535. |
| [8] | 王兆夺, 黄春长, 查小春, 庞奖励, 周亚利, 李晓刚. 淮河上游卢庄段全新世古洪水水文恢复研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(2): 325-333. |
| [9] | 唐进年, 丁峰, 张进虎, 苏志珠, 孙涛. 库姆塔格沙漠东南缘BL剖面粒度记录的全新世快速气候事件[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(6): 1171-1178. |
| [10] | 胡迎, 黄春长, 周亚利, 庞奖励, 查小春, 郭永强, 石彬楠. 黄河上游洮河流域全新世古洪水水文学研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(5): 1029-1037. |
| [11] | 李浩, 胡顺军, 王泽峰. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘梭梭茎干液流变化及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(4): 795-804. |
| [12] | 董义阳, 胡顺军, 赵成义, 朱海, 王丹丹, 丁之勇. 采用一维水平入渗试验测定古尔班通古特沙漠南缘丘间地风沙土渗透系数[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(4): 729-736. |
| [13] | 谢海超, 魏海涛, 王强, 黄小忠, 彭卫, 陈发虎. 新疆博斯腾湖全新世沉积磁性矿物组成与沉积环境探讨[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(3): 512-522. |
| [14] | 刘雯瑾, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 查小春, 周亚利, 石彬楠. 黄河马头关段全新世古洪水水文恢复及气候背景研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(1): 85-93. |
| [15] | 石彬楠, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 查小春, 刘涛, 刘雯瑾. 渭河上游天水东段全新世古洪水水文学恢复研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(3): 573-581. |
|
||
